Definition
Related Definitions
Currency Depreciation
Currency depreciation is the fall in the value of a currency relative to another currency in a floating exchange rate system. Floating exchange rate system refers to a foreign exchange system where the factors of demand and supply affect the value of the currency with minimal government intervention.
The value of a currency is always measured relative to another currency. Currency depreciation may happen because of various factors existing in the economy that move the value of domestic currency against the foreign currency. Economic decisions taken domestically also play an important role in affecting the value of a currency.
The opposite of currency depreciation is currency appreciation, where the value of a currency increases relative to another currency. Both currency appreciation and depreciation happen in a floating exchange rate environment.
Currency depreciation is different from devaluation where the value of the domestic currency is deliberately decreased by the government and central bank.
How does a currency depreciate?
Consider the following example: the exchange rate of GBP/AUD is 1.77, this means that 1 GBP is worth 1.77 AUD in the forex market. However, if the GBP/AUD exchange rate drops to 1.57 then GBP is said to have depreciated against the AUD. When the exchange rate drops to 1.57, the value of 1 GBP becomes equal to 1.57 AUD, which is lesser than the previous value of 1.77.
On the other hand, AUD is said to have appreciated against GBP, because one unit of AUD can be used to buy more GBP than what could be previously bought with it. Therefore, currency depreciates by 11.2%.
How does the supply of foreign exchange affect exchange rates?
Consider the following example showing the determination of exchange rate of Dollar in terms of Euro. The supply of Euro refers to the quantity of Euro available as foreign exchange, while the demand for Euro reflects its demand in the domestic country.
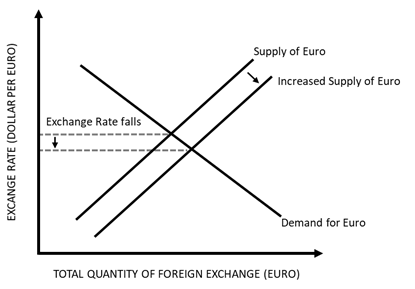
Considering the above diagram, the supply of Euro in the economy is increasing, while the demand for Euro remains the same. As more and more units of Euro are accumulated as foreign exchange, Euro depreciates while Dollar appreciates.
Therefore, the amount of foreign exchange available with a country affects the exchange rate of the domestic currency with respect to the foreign currency. As the units of foreign currency increase in a country, the value of domestic currency decreases.
What factors lead to currency depreciation?
A currency depreciation can occur because of domestic as well as international factors, these include:
- Reduction of domestic interest rates: As the domestic interest rates of Country A decrease, it becomes less attractive for foreign investors to invest in that country. Thus, they sell off their assets in Country A to invest in other countries offering a higher rate of interest.
More and more investors would demand foreign currency in exchange for the domestic currency of Country A. Thus, the demand for the domestic currency falls in the foreign market. This leads to a depreciation of the domestic currency in the international markets, while the value of foreign currency increases.
- Fall in the price of exports: As the prices of a good exported by country A falls, the foreign exchange held by the country decreases. On the other hand, the demand for domestic currency in foreign countries decreases. Therefore, the domestic currency depreciates.
- Increase in the value of imports: As the value of imports increases, there is a net outflow of domestic currency of Country A to other countries. Therefore, the supply of domestic currency increases in foreign countries. This leads to an exchange rate weakness in the domestic currency.
- Central Bank actions: If the Central Bank of Country A decides to purchase foreign assets using domestic currency, then the supply of domestic currency decreases in Country A. Therefore, this leads to a decrease in the value of domestic currency and subsequently its depreciation.
- Inflation: When there is an inflation in Country A, the value of domestic currency decreases. Thus, the domestic currency would depreciate against all other currencies internationally.
How does currency depreciation impact an economy?
Currency depreciation can lead to the following:
- Value of debt decreases: When a currency depreciates, then the value of debt instruments in the country would decrease. Thus, it becomes easier to pay off debt held by foreign countries in the domestic country as lesser amount of foreign currency is needed to repay the same amount of debt in the domestic currency.
- Increased supply of foreign products: This may lead to an increase in the productivity in the economy. As the inflow of foreign products increases, their price may eventually rise. There is also the possibility of increased competitiveness in the domestic market due to increased supply of foreign goods.
- Increased Output: As competitiveness rises in the country, it may lead to increased growth. This would lead to higher employment and higher output.
- Interest Rates: When a currency depreciates due to inflation, then the decreased value of domestic currency may lead to an increase in interest rates. As the value of a currency declines, there may be an increase in interest rates to encourage saving in the economy. Thus, there may be an upward pressure on interest rates to combat inflation.
How can depreciation harm the economy?
Currency depreciation may lead to various disadvantages for an economy:
- Due to increased foreign goods, there may be inflation.
- Depreciation may also conversely decrease output and productivity if the domestic country is not able to raise its competitiveness to match the increased supply of foreign goods.
- Domestic financial instruments may lose their value and the market for financial instruments may crash.
- Capital markets may also be impacted negatively as net outflow of capital may lead to increased prices.
