Before December 2019, SARS-CoV-2 virus, the cause of COVID-19, was not known to the science world. Pneumonia due to an undetermined reason was first reported on 31 December 2019, to the World Health Organization (WHO), after a few cases emerged in Wuhan, China.
With the number of coronavirus disease (COVID-19) cases climbing steeply everywhere, overburdening one hospital after another and pushing the global death toll to almost 63,000 (according to WHO), the sprint to discover the cure has accelerated dramatically.
Vaccine or treatment to stop the novel coronavirus, severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2 (SARS-CoV-2), could save the lives of severely infected individuals, protect medical practitioners and others at high risk of infection, and lessen the time patients spend in hospitals.
According to the International Monetary Fund (IMF), the COVID-19 pandemic has hit economies hard, and one more time, the globe has entered a recession, worse than the one experienced in 2009.

The healthcare industry across the globe is in the race of developing medicine to combat COVID-19. Moreover, during this pandemic, the healthcare agencies are releasing guidelines, including the recommendations to prevent the spread of COVID-19 and the protective measures to be adopted.
To Know More Do Read: Ray of Hope amid Coronavirus- Potential Vaccine For COVID-19 is Underway
In this article, we will acquaint you with a few critical points from COVID-19 guidelines:
Enforcement Policy for Face Masks and Respirators During COVID-19
The US Food and Drug Administration (FDA) plays a significant role in safeguarding the US from risks, including emerging infectious diseases such as the COVID-19 pandemic. It is noteworthy that the FDA is dedicated to delivering timely guidance for endorsing response attempts to this threat.
The agency has announced this guidance to provide a program for increasing the availability of general use face masks for the public and facepiece respirators for medical professionals during the pandemic.
Moreover, according to the Department of Health and Human Services and the Public Health Services (PHS) act, this policy is envisioned to remain effective only for the duration of the public health emergency related to COVID-19.
Besides, the CDC continues to analyse the spread and impact of the coronavirus across the US. The CDC issued new guidelines advising that in the US, people should wear homemade face masks to prevent the spread of the disease. According to some experts, if individuals cover their faces with a homemade cloth mask or any other barrier, it might diminish the number of particles laden by the virus they circulate.
Maintaining Essential Health Services and Systems
COVID-19 is straining health systems across the globe. The quickly escalating requirement of health facilities and healthcare practitioners threatens to leave some health systems overloaded and unable to function adequately.
Previous outbreaks have demonstrated that when medical systems are devastated, both direct mortality from a pandemic, and indirect mortality from vaccine-preventable and curable situations rise significantly.
All nations will need to make tough decisions for balancing the challenges to respond to the threat directly. At the same time, they are employing in strategic development and coordinated action for maintaining the necessary medical service delivery along with alleviating the risk of any interruption in system.
During the Ebola outbreak (2014-2015), the increased number of fatalities triggered by malaria, measles, HIV/AIDS, and tuberculosis due to the failure of the health system were higher than the casualties from Ebola.

To aid nations to find a way during these challenges, the WHO has updated operational planning guidelines in balancing the requirements of responding directly to coronavirus infection while maintaining essential health service supply and alleviating the risk of system collapse.
Early investigations protocols
It is crucial to perform early clinical and epidemiologic studies to carry out early investigations in an outbreak of the virus. The latest emergence of new coronavirus indicates that understanding of transmission patterns, clinical features, severity, along with risk factors for infection remains inadequate, whether among the general population, for medical practitioners or in the household as well as other “closed” locations.
These protocols have been intended accumulate and communicate information quickly and thoroughly in a structure that enables collection, tabulation as well as analysis throughout different settings worldwide.
Moreover, WHO mentioned that the agency urges all countries as well as study centres to participate in the effort irrespective of the availability of resources or volume of patients. The primary data ownership remains resolutely with the individual nations and/or sites.
Several early investigation master procedures or forms for COVID-19 that are accessible for countries, are highlighted below:
- The first few COVID-19 X cases and contacts transmission investigation protocol (FFX).
- Assessment of risk factors of COVID-19 among Health workers protocol.
- Age-stratified seroepidemiological inspection procedure based on population for COVID-19.
- Surface sampling of COVID-19 virus- A practical how-to procedure for healthcare and public health experts.
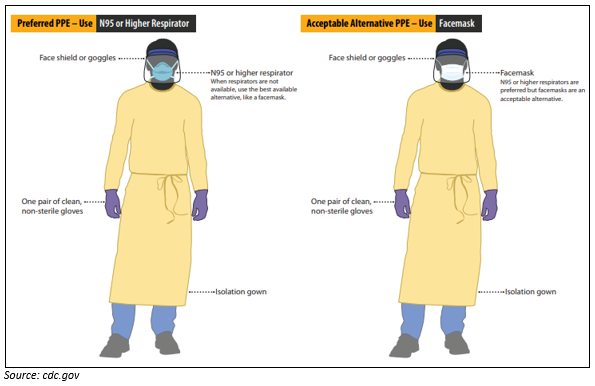
Use Personal PPE while Caring for Patients with Confirmed or Suspected COVID-19
Before caring for patients with confirmed or suspected coronavirus cases, healthcare professional (HCP) should-
- Receive comprehensive training on when and what personal protective equipment (or PPE) is necessary, how to put it on and take it off, its limitations, and proper care, maintenance, and disposal of PPE.
- Demonstrate competency in performing appropriate infection control practices and procedures.
Infection Prevention and Control
Healthcare-associated infections (HAI) are one of the most common adverse outcomes in care delivery and a central public health problem with an impact on morbidity, mortality and quality of life. At any point in time, up to 10 per cent in developing and 7 per cent of infected individuals in developed countries will acquire at least one HAI.
These infections also represent a substantial burden on the economy at the societal level. However, a significant percentage of these infections (HAIs) are preventable through efficient infection prevention and control procedures.
WHO advises member states to enhance hand hygiene procedures broadly to help prevent the transmission of the COVID-19 virus by:
- Providing universal access to public hand hygiene stations and making a compulsory use on their entering as well as leaving any private or public commercial firm and any public transportation capacity.
- Enhancing access to facilities and practices of hand hygiene in medical care facilities.
Through the course of this pandemic, every individual should stay safe and follow the guidance provided by healthcare agencies until the development of a vaccine, and focus on how to boost their immunity to fight with coronavirus infection if unfortunately, they get infected.
Want to know how to boost immunity during this pandemic? Do Read: Ways to Boost Your Immune System to Combat COVID-19