Definition
Related Definitions
Underlying Asset/Security
What is underlying asset?
An underlying asset means the primary component depending on which a derivative instrument gets its value. Another name for the underlying asset is the underlying security. Take, for example, a gold ETF that derives its value from gold as an underlying commodity. Investors can use an underlying asset to identify the basis of movements and demand, supply trends of a derivative contract. Take, for example, an option contract share of Apple Inc. derives valuation from the future predictions of the underlying stock of Apple Inc.
Highlights
- All derivatives derive their value from underlying assets.
- Primarily they help investors and traders to perform hedging and arbitrage.
- All types of underlying assets and their derivatives are subject to various investment risks, and it is a major criterion for their classification.
- Underlying assets are highly speculative and sometimes lead to huge losses for investors if not appropriately studied.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQ)-
How is the underlying asset used?

Source: © Djbobus | Megapixl.com
There may be several types of derivatives that are trading in the financial markets. However, all of them derive value from an underlying asset or underlying security. It means that the price of the derivative is affected by the price volatility of the underlying security. Moreover, an underlying can be any financial instrument, right from a commodity to index or even a share or another derivative. The higher the complexity of underlying, the higher is the complexity of the derivative’s pricing. Different underlying assets hold relationships with derivatives; the following basic formula can explain it.
Underlying asset formula
They can be expressed in generalised terms of basic mathematical expression as displayed below: –
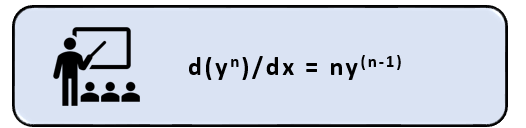
Source: Copyright © 2021 Kalkine Media
Here,
The underlying asset is expressed as yn.
The formula, when applied to an underlying asset, would result in a derived value.
The derived value is expressed as ny(n-1).
The formula may vary as things become complex.
Usually, the underlying asset trades at the spot market, where investors need to make a full upfront payment to acquire the asset (trade is settled in 1-2 days). In the case of derivatives based on underlying assets, there is no requirement to pay a 100% upfront payment. Investors can take exposure to derivatives based on the underlying securities just upon payment of a margin.
What are the types of underlying securities?
The easiest way to classify underlying assets or securities is to categorise them as one of the following-
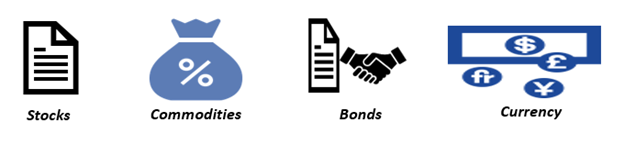
Source: Copyright © 2021 Kalkine Media
Underlying securities are typically classified by the type of investment risks they carry. While Commodities and stocks entail market risks, currencies and commodities have inherent economic risks. Investors give the investment risks priority. Default Risk, credit risk, and interest rate risk are all considered for classifying underlying assets.
Example-
Financial derivative or stock options that derive their value based on actual underlying stock.
- There can be instruments that derive value from commodities (such as gold, oil, or cotton).
- Another kind of derivative is based on the interest rates held by an underlying bond.
- Currencies are also underlying assets that influence the price of financial derivatives like forwarding contracts, credit default swaps (CDS), and collateralised debt obligations (CDO).
Investors and businesses very commonly use them to hedge their risks in international markets.
What is the significance of underlying asset?
- An underlying asset is necessary to define the price of a derivative. It enables investors to use the value for identifying and forecasting price trends.
- It is the defining criteria to finding hedges for risks.
- By buying derivatives, investors are often trying to limit downside risks, and at the same time, allowing unlimited upside potential.
- It is the basis of the speculation of a derivative instrument.
For example, when investors purchase commodity derivatives to speculate on future commodity price movements, they are trying to limit downside risk on adverse commodity prices while allowing for unlimited potential for gains on it.
What are the various advantages of an underlying asset?

Source: © Iqoncept | Megapixl.com
- Trade positions covered by an underlying asset are less risky to hold as predicting underlying security prices is more effortless.
- A few types of underlying assets are highly marketable. They have a market that promotes liquidity and exchange.
- Many investors use the underlying assets to earn high returns.
- Underlying assets provide hedging and arbitrage benefits to some extent. Especially currencies and commodities.
- As derivatives with underlying are traded in an organized market, the transaction costs involved are relatively meagre.
What are the various disadvantages of an underlying asset?
Some of the disadvantages are as follows.
- Investors can utilise a few underlying securities for speculative purposes leading to huge losses.
- Almost all kinds of underlying assets pose some risk.
- Many derivatives can only be traded and settled on the over-the-counter markets, which is a limiting factor for investors who want to have liquidity.
- Some underlying assets may have high counterparty risk.
- An underlying securities performance needs to be monitored periodically.
- They are prone to information asymmetry.
