Summary
- German industrial output plunged by 17.9% in April (the biggest drop since records began in 1991), due to coronavirus shutting down Europe’s biggest economy.
- The auto industry reported the sharpest plunge of 74.6% (month on month basis).
- Exports plunged far more than expectations by 24% in April, while imports dropped 16.5% due to drying up of demand amid coronavirus lockdown.
- GDP of Germany is projected to contract by 10% in Q2 of 2020, and production levels will decline in the coming 3 months but at a slower pace, as per market reports.
The industrial output in Germany displayed a record fall in April as the coronavirus outbreak resulted in the shutdown of production by manufacturers in the biggest economy of Europe.
As per the figures released by the statistics office of Germany, the German industrial output shrank by 17.9% in seasonally adjusted terms in April compared to March. The industrial production declined by 25.3% compared to April 2019. Destatis, the statistics office of Germany confirmed that the drop in output was the most significant fall since the beginning of the time series in January 1991.
Germany has reported 186,516 coronavirus cases with 8831 deaths, as on 10 June 2020. However, the country has far less spread of epidemic than its counterparts in Europe, recording a lesser death toll compared to its peers.
Industrial statistics shrank for April
As per Destatis’ latest update, production in industry excluding energy and construction fell by 22.1% in April 2020. While the production of intermediate goods fell by 13.8%, consumer goods and capital goods production dropped by 8.7% and 35.3% within the industry. The automotive sector witnessed the sharpest fall of 74.6% month on month.
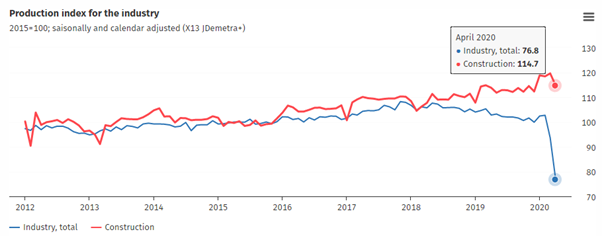
Source: Destatis, 2020
Germany has performed better than many of its counterparts with a fall of 2.2% in total economic output in the first 3 months of 2020. The lockdown measures adopted in the country have been much less severe than those in Spain, Italy and France. Germany never ordered the closure of factories, but many companies stopped production in a few sectors like car manufacturing disturbing the supply chains.
As per the Economic Ministry, coronavirus induced restrictions took a toll in April as measures to contain coronavirus spread were applied from mid-March.
Germany started to lift its lockdown measures on 20 April, permitting smaller retailers and car dealerships to resurrect. Production of cars was allowed to restart from April-end, whereas additional controls like reopening of schools were relaxed during early May. The country also plans to lift travel restrictions to other European nations by 15 June.
Exports plunged as COVID-19 wipes out demand
As per Destatis’ June update, Germany’s exports, as well as imports, tumbled down declaring their most significant decreases since records started in 1990 during April. The plunge came due to drying up of demand amid coronavirus lockdown producing further pessimism in the outlook for the country.
Exports reported a 24% fall (in seasonally adjusted terms), exporting goods to the value of 75.7 billion euros, surpassing expectations of numerous economists. In comparison, imports dropped 16.5% and importing goods to the value of 72.2 billion euros in April compared to the previous month. As per the Federal Statistics Office, the trade surplus of the country dwindled to 3.2 billion euros.
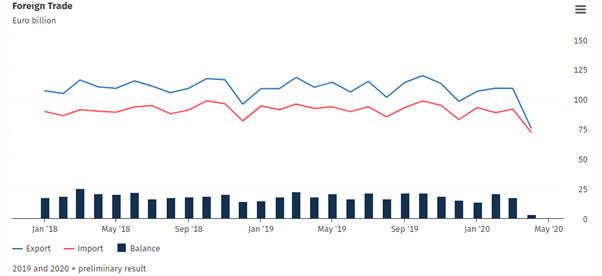
Source: Destatis, 2020
Market experts had projected exports and imports to drop by 15.6% and 16%, respectively. The speed of recovery remains contingent on its trade allies and European counterparts like the US, France and China along with logistics like opening up of borders and supply chains.
ALSO READ: China’s road to recovery: Production levels up, but demand remains muted
Outlook ahead
The April data (industrial output) has confirmed the anticipation of Germany posting its steepest fall since World War 2 in Q2 2020.
Thomas Gitzel, VP Bank Group Economist, stated that the GDP of Germany would contract by more than 10% in Q2. He also added that the low point had been touched. As production resumes in the automotive sector and protective measures ease, economic recovery is set to begin.
Germany’s governing coalition has agreed on a sweeping $130 billion euros in fiscal stimulus measures which includes tax breaks and subsidies to buy electric vehicles to surge consumer spending and investments in the business. Based on this assumption, the Government of Germany has predicted that the GDP of the country will shrink by 6.3% for 2020 as a whole.
Klaus Wohlrabe, Economist at ifo (Institute for Economic Research), there are increasing expectations by manufacturers that production levels will fall in the coming 3 months but at a slower pace even after the stimulus package.
ifo’s index of production expectations rose to -20.4 points in May having stood at -51 points in April. The institute noted that although this marks the most significant month on month increase since the German reunification 30 years ago, it implies the plunge in production is levelling now.






