Highlights
- Hydrometallurgical test results have shown encouraging recovery rates, with zinc (Zn) at >96% and vanadium (V) at 91.1%.
- Recovery for REEs, including neodymium (Nd) at 68% and europium (Eu) at 90.3%, has been achieved.
- Ongoing metallurgical testing focuses on optimising leach conditions for maximum recovery.
- A scoping study based on recent results is expected to be completed later in 2025.
- The company secured AUD 47,465 R&D tax incentive rebate and raised AUD 54,744.
Mount Burgess Mining NL (ASX:MTB), an exploration and development company focused on polymetallic deposits, has released its quarterly report for the period ended 31 March 2025. The report outlines key progress on metallurgical testing at its Nxuu Deposit, particularly in the recovery of vanadium (V), gallium (Ga), germanium (Ge), and rare earth elements (REEs), using advanced hydrometallurgical processes.
Metallurgical Test Work on Nxuu Deposit Samples:
During the March quarter, Mount Burgess continued metallurgical test work on samples from the Nxuu Deposit.
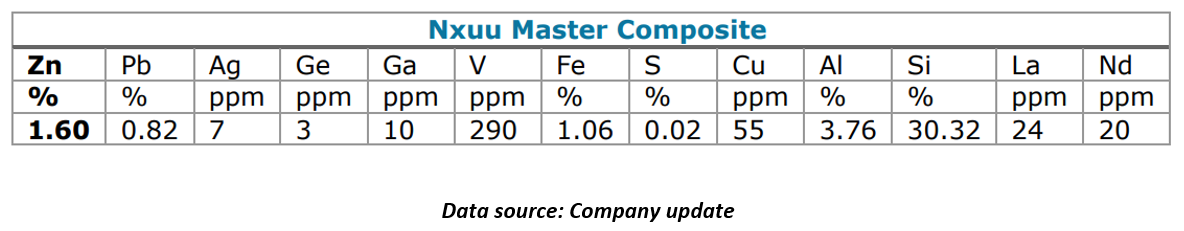
The interim results from these tests have been encouraging, indicating a high potential for efficient recovery of a range of valuable minerals. The test work focuses on optimising the recovery process of metals such as zinc (Zn), lead (Pb), vanadium (V), gallium (Ga), germanium (Ge), and several REEs.
Hydrometallurgical Test Work Results:
The latest hydrometallurgical test results for the Nxuu Deposit have delivered encouraging findings:
- Zn: >96% recovery
- Pb: 79.4% recovery
- V: 91.1% recovery
- Ga: 59.3% recovery
- Ge: 77.3% recovery
The current phase of metallurgical testing is designed to improve leaching kinetics. The company has been experimenting with parameters, including pressure, temperature, and pH, to optimise the extraction process. This ongoing evaluation is expected to lead to even better recovery results.
Leach tests on a master Nxuu composite were conducted in March 2025, with the results received after the quarter end.
 Key Rare Earth Elements Extraction:
Key Rare Earth Elements Extraction:
The extraction of rare earth elements is a critical part of Mount Burgess’ strategy to unlock the full potential of the Nxuu Deposit.
The latest results from leaching tests show the following extraction percentages for several key REE elements:
- Lanthanum (La): 69.1% extraction
- Neodymium (Nd): 68% extraction
- Praseodymium (Pr): 70.1% extraction
- Cerium (Ce): 63.3% extraction
- Samarium (Sm): 63.6% extraction
- Europium (Eu): 90.3% extraction
Further work is being carried out to improve the recovery rates of Ga, Ge and other REEs. The company continues to focus on refining the process to optimise recoveries across all targeted minerals.
Challenges and Future Steps:
Due to the highly oxidised nature of the Nxuu deposit, high dissolution of aluminum (Al), silicon (Si), and potassium (K) has been observed, which can impact the efficiency of the leaching process. Mount Burgess is addressing these challenges through continued testing and optimisation of the recovery methods.
The results from these metallurgical tests will feed into an upcoming scoping study, which is expected to be completed later in 2025. This study will further evaluate the potential of the Nxuu Deposit, including the financial and technical aspects of bringing the project into production.
Corporate Developments:
In addition to the ongoing exploration and test work, Mount Burgess NL has made significant corporate progress. In January 2025, the company received an R&D tax incentive rebate of AUD 47,465. In April 2025, the company raised AUD 54,744 through the issuance of 12,165,249 ordinary shares to sophisticated and professional investors. These shares were listed on the ASX on 24 April 2025. The funds raised are earmarked for further project development costs, including continued metallurgical test work, and for general working capital.
Shares of MTB traded at AUD 0.005 on 01 May 2025.






