Definition
Related Definitions
Assets
What is an asset?
An asset is an item that is invested in with the intention of gaining future benefits from it. An asset can be any item that holds monetary value. Any individual or organisation can own an asset that promises them a future financial benefit or a stream of income.
Assets can be tangible or intangible. For instance, land is an asset as it can be loaned out in exchange for rent. Similarly, a patent, which is intangible, can also be considered as an asset as it provides monetary value to the owner of the patent.
How is an item categorised as an asset?
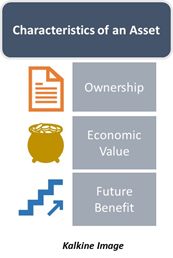
All assets hold three fundamental properties that set them apart from any other type of holdings or investments by firms and individuals. These include:
- Ownership: Assets involve the concept of ownership. The owner of the asset must pay for it and should benefit from the future income stream. This ownership is what allows the owner to gain monetary benefits from the asset.
- Economic Value: Assets are items that hold some form of monetary value and are not entirely worthless. This is important because an item can only be sold, loaned, or exchanged in the market when it holds some value.
- Future Benefit: This quality is what sets an asset apart from any other item purchased by an individual or a company. For any resource or object to be categorised as an asset for the owner, there must be a stream of income that it promises in the future. For instance, an individual might consider a family heirloom as an asset. However, the economic value associated with it might not be much. So, if the heirloom were to be exchanged in the market, it would not be of any benefit to the owner. Hence, it is not an asset.
What are the types of assets?
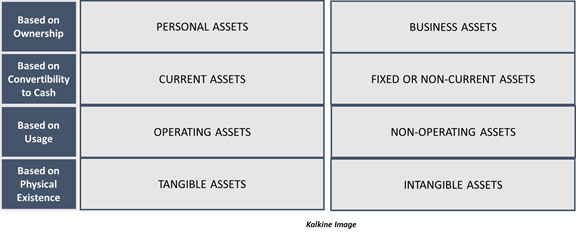
Assets can be divided into various types based on different categorisations. Broadly, assets can be divided into the following types:
- Personal Assets: These are the assets owned by individuals or households, and they generate some value for the owner. These may include property, jewellery, physical cash and cash equivalents, savings accounts, and investments such as bonds, pensions, mutual funds, etc.
- Business Assets: These assets are held by companies and are held with the intention of generating profits. These assets are added in the balance sheet of a company while the liabilities are subtracted from them. Assets may serve different purposes in a business. Individual businesses may use physical assets like machinery and equipment to produce output.
While other intangible assets can be used for profit generation in the future, simply by selling them, for instance, a company might sell the intellectual property rights of one of their products to gain profits from them.
Based on how easily the assets can be converted into cash, they can be further categorised into different types:
- Current Assets: Assets that can be easily converted into liquid money are current assets. The time frame for this conversion is typically under a year. These may include cash and cash equivalents, account receivables, inventory, marketable securities, short-term deposits.
These assets help finance the day to day operations of a business and thus, are easily convertible into liquid money.
- Fixed or Non-Current Assets: These assets can not be easily converted into cash. They are typically used in the production process and can last more than a year. They are recorded in the balance sheet under the headings “property, plant and equipment”. They are long term assets and are generally tangible assets. Some examples of fixed assets include building, vehicles, machinery, office furniture.
Assets can be categorised based on their usage into Operating and Non-Operating Assets. Operating assets are the assets used daily, while Non-Operating Assets are not used as frequently but are still crucial for a business. Operating assets would include cash, machinery, equipment patents, etc. In comparison, non-operating assets would consist of short-term investments or land or real estate that might come in usage later and do not have an immediate requirement.
Assets may also be categorised based on their physical existence into tangible and non-tangible assets. Tangible assets are physical assets like land, building machinery, inventory, while intangible assets may include various other aspects of a business that do not have a physical existence like goodwill, copyrights, trademarks, licenses and permits, intellectual property, etc.
How are assets valued?
The value of an asset held by an individual or an organisation at a time may not be equal to what it was at the time when it was bought. The value of an asset is affected by factors like depreciation and fair value.
In case of a physical asset, depreciation is the wear and tear that an asset undergoes with the course of time. However, depreciation can be generalised as the process of spreading the cost of an asset over time. It decreases the value of an asset or an item over time.
Fair value refers to the market value of an asset at a point of time. If an asset of a company was to be sold in the market five years after it was bought, then the fair value of the asset refers to the amount that it would sell for at that point. This value is derived through the process of fair market value analysis, where prices of other assets are compared to the asset in question. Some professionals are skilled at calculating fair value.
