Australian sugar market mainly constitutes raw sugar and refined sugar from sugarcane. It is vital to quote that around 85% of all produced sugar is exported as bulk raw sugar, making Australia 2nd world’s largest raw sugar exporter and it takes 3rd position right after Brazil and India in the processed sugar market. About 95% sugarcane cultivation in the country is mainly coming from the Queensland region and the remaining 5% from New South Wales.
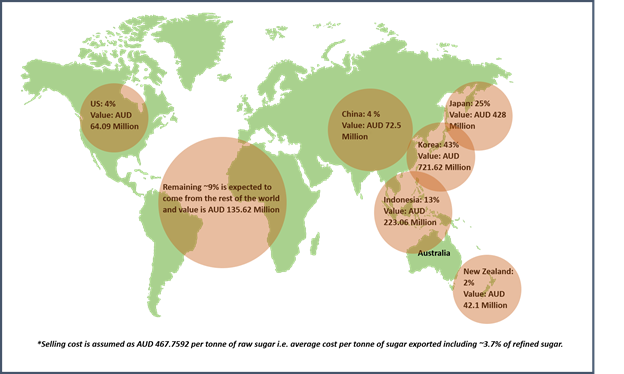
The sugar production in Australia has contributed around ~2.32%, ~2.56% in world total production amid FY18 and FY191 respectively and expected to be in the same range from ~2.51% in FY20 as estimated by Australian Bureau of Agricultural and Resource Economics and Sciences (ABARES). Whereas, the share in total export stands around ~6.4% in FY18 and expected to be same for FY19 i.e. ~6.42% followed by ~6.17% in FY20. The top export market for Australian sugar is South Korea, Indonesia followed by Japan and Malaysia.
Australia has contributed around ~2.32%, ~2.56% in total sugar produced globally in FY18 and FY191 respectively and is expected to be in the range of ~2.51% in FY20 as estimated by Australian Bureau of Agricultural and Resource Economics and Sciences (ABARES). Whereas, the share in total export stands around ~6.4% in FY18 and is expected to be same for FY19 i.e. ~6.42% followed by ~6.17% in FY20. The top export market for Australian sugar is South Korea, Indonesia followed by Japan and Malaysia.
Australian agricultural export market as of FY18
Source: Australian Bureau of Agricultural and Resource Economics and Sciences (ABARES) and Kalkine Research
The volume of export in FY19 has fallen by around ~6.2% from the previous year and it is anticipated to fall further by ~2.4% in FY20 to 3.663Mt. Similarly, production is likely to plunge by 4.4% in FY20 to 4.518Mt from FY19 due to the lower yields because of dry weather. The producing land has decreased by ~2.3% from FY18 to FY19 and it is expected to further plunge by 1.3% in FY20. In FY18, a total of 389 thousand hectare of land was under cultivation which is anticipated to shrink to 375 thousand in FY20.
How are other countries doing in FY20?
As per United States Department of Agriculture, the global sugar production is expected to tumble by ~3.6% to 176Mt in FY20 mainly due to the 5Mt of production cut coming from India following lower area for cultivation and falling yields.
The top two producing countries are Brazil and India.
Brazil: The sugar production in FY20 is expected to fall and reach around 29.4Mt. The fall is mainly due to the use of sugar cane toward the production of ethanol and the percentage of the total sugarcane output used for sugar is likely to fall from 35.9% to 35%. The export market is forecast to drop from 19.6Mt in FY19 to 18.6Mt in FY20, the lowest in the last twelve years.
India: As discussed 5Mt of production plunge is anticipated in FY20 to 29.3Mt. Whereas the consumption is likely to grow to 28.5Mt due to the rising economy. Despite the short margin of production and consumption, India is set to export around ~5Mt in FY20 due to the subsidy over marketing expenses such as handling, upgrading processing costs, and freight charges.
Trade dispute at the World Trade Organization (WTO) due to India’s Sugar Subsidy
India has approved a subsidy of INR 10,448 i.e. USD 145.58 per tonne for exports in the FY20, to boost the sugar supplies and to encourage the mills to close the deals in the overseas market. This push by India is intended to prevent the exploitation of around 35 million impoverished farmers in the country.
However, this subsidy took an alleged turn when Brazil, Australia and Guatemala pointed out that the subsidy is crossing the limit provided for domestic support by WTO Agriculture Agreement and hurting global sugar prices and producers. While India insists that the subsidy is within WTO obligation and has no impact on global prices or to distort trade.
The expected 150% rise in Indian sugar export from 2Mt in FY19 to 5Mt in FY20 would exceed the last highest export of 4.7 Mt in FY08. Apart from the subsidy, devaluating INR in terms of USD could favour exports in the coming years.
Anticipated FY20 Global Production:

“The fall in global production with strong consumption is likely to increase the sugar price in the near future.”
Sugar Price Outlook
As per ABARES, the price of sugar (raw equivalent) is expected to increase by 1.2% in FY20 from FY19 to 12.5 US cents/lb. With the increase in price, the return to cane growers too is expected to increase from 35.1 A$/t in FY19 to 35.6 A$/t in FY20.
Also, the world sugar price indicator i.e. Intercontinental Exchange, Sugar no. 11 future contract for raw sugar as well as Intercontinental Exchange, the White Sugars future contracts for physical white sugar has shown increasing trends in future contracts.
The impact of bushfire on the sugar production is yet to be ascertained. The sugar market participants and producers are watching this development closely.
As of 10th January 2020, the details of the futures contracts are:
1 FY19 values are estimated by ABARES
Disclaimer
This website is a service of Kalkine Media Pty. Ltd. A.C.N. 629 651 672. The website has been prepared for informational purposes only and is not intended to be used as a complete source of information on any particular company. Kalkine Media does not in any way endorse or recommend individuals, products or services that may be discussed on this site. Our publications are NOT a solicitation or recommendation to buy, sell or hold. We are neither licensed nor qualified to provide investment advice.






