Summary
- The pandemic has accelerated the need for digitalization among Canadian banks
- What we see emerging is a fusion of technologies, including automation, machine learning, blockchain, robotic processes and open banking
- From seamless customer experience to a quick TAT, banks must ensure the evolution of their products, services, and processes to stay ahead of the curve
Despite the influx of cognitive and new-age digital resources, the retail banking model has primarily remained the same since the days of 15th century Italian bankers.
But that was until COVID-19.
The pandemic has accelerated the need for digitalization and financial inclusion utilizing mobile channels and digital payment systems. And banks in Canada have taken note.
Financial institutions are now reassessing their business models in a ‘homebody economy’ to ensure profitability and sustainability, and how digital transformation can drive growth and efficiency.
The multimillion-dollar question banking industry should ask themselves right now is:
How do we survive and thrive in this stay-at-home financial ecosystem?
Currently, the banking landscape has a multi-faceted channel approach, as shown below:
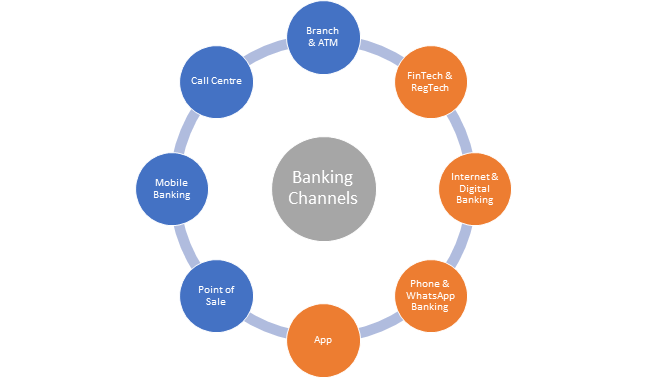
But recent developments during pandemic, including change in policies and regulations, and technological disruptions, are compelling banks and financial institutions to push their boundaries. Increased attention is now being devoted to digital governance and sustainable development – the two key enablers in the future of banking.
Global investments in banking technologies such as FinTech and Payment Banks have also grown exponentially in the last couple of years. Canada, a part of this rapidly-growing advanced banking ecosystem, acknowledges the importance of transforming banks into technologically modern and agile organizations.
Banking Beyond COVID-19
The coronavirus pandemic has unleashed a new wave of disruption, way more powerful and widespread than what we have seen in recent years. Digital technology, perceived as the driver of disruption in a pre-COVID world, has now turned a savior.
What we see emerging is a fusion of technologies, including automation, machine learning, blockchain, robotic processes and open banking.
Future Trends in Banking
1. Accelerated Digital Transformation
Banks need to embrace omni-channel digital banking platforms to accelerate digital transformation. This includes:
- Streamlining banking infrastructure
- Unifying traditional core systems with new-age FinTech capabilities
- Enhanced customer experience through seamless digital channels
- Automating compliance tasks
- Real-time management of information
- Reducing operational risks
Top six Canadian banks spent over C$ 90 billion on technology between 2009 and 2018 according to a media report, a bet that is beginning to pay off in this the pandemic world.
2. Open Banking Ecosystem
Banks needs to take a leap of faith to open an application program interface (API) economy to foster innovation, generate better return on equities and expand revenue channels. This means adapting open banking that is enabling trusted third parties to access bank accounts.
As per a PwC Canada report, open banking will help financial institutions see the complete picture of customers’ creditworthiness through their bank account activities.
3. FinTech Adaptation
Financial Technology or FinTech has challenged the status quo of financial services industry the world over. For banks, this means radically changing the cost of financial intermediation, eroding lenders’ profit margins. Adapting to this new tech (through partnerships or in-house products) will not only open up avenues for new sources of revenue, but also allow banks to compete with lean, agile and innovative fintech startups.
The total transaction value in digital payments segment in Canada is expected to reach US$ 52,934 million by 2020, says data firm Statista.
4. Cybersecurity Plan
Building a cyber-resilient strategy is critical for the financial industry. From securing mobile banking and payment channels to financial transactions, banks must implement security controls to reduce gaps, which can be exploited during a singular moment of vulnerability or exposure. From neutralizing attacks before they escalate into a crisis to creating robust data backups, crisis management must exist. Undertaking risk assessments and disaster recovery can help banks ensure business continuity while keeping costs down is imperative.
A Ryerson University cybersecurity survey of 2,000 adults in May claimed that at least 57 per cent participants have faced at least one cybercrime.
5. Leveraging RegTech
Regulatory Technology or RegTech helps companies understand the rules and manage their risks. RegTech firms, born after the financial crisis of 2008 that enforced strict financial regulations, focus on risk management and compliance with regulatory framework through efficient technology.
Adapting to the RegTech universe means leveraging the plot of regulatory ecosphere and create a supportive environment for innovation. It not only gives insights on regulatory policies but helps consolidate position in robust financial markets, thereby broadening the financial services infrastructure to meet future opportunities.
6. Cloud, SaaS and Cognitive Intelligence
Cloud and software-as-a-service (SaaS) have changed the banking interface, allowing them to operate with agility and speed usually associated with FinTech competitors. From accelerating digital banking innovation to creating sustainable revenue streams, new-age cognitive intelligence is augmenting secure, efficient and faster banking systems with reduced costs and capital requirements. Cognitive intelligence helps detect key patterns from billions of data sources in real-time, deriving actionable insights. Some may also refer to this as Big Data. In short, cognitive intelligence enables analysts to stay ahead of the curve.
Equitable Bank’s digital platform EQ Bank has surpassed $3 billion in deposits by scaling their cloud offerings.
7. AI & Robotic Process Automation
There is a storm brewing in the AI world – convergence of vast amounts of data with supercomputing powers. Robotic processes help create or train algorithms, where machines are capable of self-learning with minimal or no human intervention.
For instance, voice-based “intelligent personal assistants” such as Amazon Alexa or Google Home –use machine learning and natural language generation (NLG) algorithms to get smarter.
Smaller administrative tasks such filling up forms, etc., are already being undertaken with robotics automation. While robotic processes automation is still in a nascent phase, it is a space to watch out for.
8. New-world Blockchain
Blockchain is an open, distributed ledger technology (DLT) that stores information, enabling transactions between parties efficiently. Involved parties share digital ledgers through digital network sans involvement of any central authority. It is secure, fast and transparent. In banking ecosystem, blockchain can provides a tamper-proof environment through DLT, providing an impenetrable record of transactions that can be tracked real time.
The Way Ahead
Innovation and forward-thinking continue to be the key driving factors for financial institutions caught between an upended world economy, digitalization and growing costs. Other key imperatives include revenue and profit generation, financial resilience, business growth and shareholder value.
In a bid to meet the demands of new age tech-savvy customers, financial institutions are adapting transformation and incorporating innovation.
From seamless customer experience to a quick turnaround time, banks must ensure the evolution of their products, services, and processes to stay ahead of the curve.