Highlights:
- Definition of On-the-Run Bonds: An on-the-run bond refers to the most recently issued government bond within a specific maturity range, which is generally the most liquid and actively traded security in that category.
- Importance in Financial Markets: On-the-run bonds serve as key benchmarks for interest rates, influence pricing for off-the-run bonds, and provide insights into market sentiment and economic conditions.
- Liquidity and Pricing Differences: Due to their high demand and liquidity, on-the-run bonds typically trade at a premium with lower yields compared to older, off-the-run bonds, which are less liquid.
In the world of fixed-income securities, government bonds play a crucial role in determining interest rates, influencing investment decisions, and managing financial risk. Among these bonds, on-the-run bonds hold special significance as they represent the most recently issued bonds within a specific maturity range. These bonds are characterized by their high liquidity, tight bid-ask spreads, and frequent trading activity, making them the preferred choice for investors, institutions, and governments alike.
The concept of on-the-run vs. off-the-run bonds is fundamental for bond market participants, as it helps differentiate between newer, more actively traded securities and older issues that have lower liquidity. In this article, we will explore the concept of on-the-run bonds, their advantages, their role in the financial markets, and key factors influencing their demand and pricing.
What Are On-the-Run Bonds?
On-the-run bonds refer to the latest government bond issues within a given maturity range. These bonds are the most current versions of a particular bond series and are typically considered the benchmark securities for their respective maturities. Governments, such as the U.S. Treasury, regularly issue bonds to finance public spending, and each new issuance replaces the previous one as the "on-the-run" bond.
For example, if the U.S. Treasury issues a new 10-year Treasury bond, it becomes the on-the-run bond for the 10-year maturity category. The previous 10-year bond, now considered an off-the-run bond, will still be available for trading but with significantly lower liquidity and trading volume.
Key Characteristics of On-the-Run Bonds:
Liquidity: These bonds are the most liquid in the market, with high trading volumes and ease of buying or selling.
Benchmark Status: On-the-run bonds serve as benchmarks for pricing other debt instruments and derivatives.
Tight Bid-Ask Spreads: Due to their demand, they have minimal differences between buying (bid) and selling (ask) prices.
Lower Yields: On-the-run bonds tend to offer lower yields compared to off-the-run bonds because of their popularity and high demand.
Importance of On-the-Run Bonds in Financial Markets
On-the-run bonds play a critical role in the functioning of the financial markets due to their status as benchmark securities. Their influence extends across various segments of the financial system, including monetary policy, investment strategies, and risk management.
- Benchmark for Interest Rates:
On-the-run bonds are widely used as a benchmark to set interest rates for other financial instruments, such as corporate bonds, mortgages, and derivatives. For instance, the yield on a 10-year on-the-run U.S. Treasury bond serves as a key indicator for economic health and long-term interest rate expectations.
- Price Discovery and Market Sentiment:
The prices of on-the-run bonds provide insights into investor sentiment and expectations regarding inflation, economic growth, and Federal Reserve policies. A rise in demand for these bonds can signal a risk-averse market, whereas a decline may indicate rising interest rate expectations.
- Hedging and Trading Strategies:
Institutional investors and hedge funds often use on-the-run bonds for hedging purposes or as part of trading strategies due to their deep liquidity. They are commonly involved in short-term trading, arbitrage, and repo (repurchase agreement) transactions.
On-the-Run vs. Off-the-Run Bonds
Understanding the difference between on-the-run and off-the-run bonds is crucial for investors looking to optimize their bond portfolios.
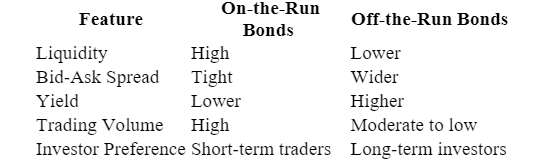
Key Takeaways:
- On-the-run bonds are suitable for traders seeking quick execution and price efficiency.
- Off-the-run bonds may offer better yields for long-term investors willing to accept lower liquidity.
Why Are On-the-Run Bonds More Expensive?
One of the distinguishing factors of on-the-run bonds is their higher prices compared to off-the-run bonds of similar maturities. This price premium exists due to several reasons:
Increased Demand: Investors, institutions, and governments prefer the latest bond issue due to its benchmark status and high trading volumes.
Lower Risk of Price Impact: The high liquidity reduces transaction costs and minimizes the impact of large trades on prices.
Repo Market Utility: On-the-run bonds are widely used in the repo market, where institutions use them as collateral for short-term borrowing.
Since on-the-run bonds are highly sought after, they usually trade at a lower yield, meaning investors accept lower returns in exchange for ease of trading and security.
How On-the-Run Bonds Impact Portfolio Management
Investors and fund managers incorporate on-the-run bonds in their portfolios for various strategic reasons:
Liquidity Management: On-the-run bonds allow investors to quickly enter or exit positions with minimal impact on market prices.
Benchmark Comparisons: Institutional portfolios often track their performance against benchmark bonds such as the latest U.S. Treasury issues.
Diversification: These bonds can provide stability and risk reduction in a diversified investment portfolio.
However, investors seeking higher yields may consider off-the-run bonds, which offer better returns but come with lower liquidity and wider spreads.
Risks Associated with On-the-Run Bonds
Despite their popularity and liquidity, on-the-run bonds are not without risks. Some of the key risks include:
Market Volatility: Changes in interest rates or economic conditions can lead to sudden price fluctuations.
Lower Yields: Investors may face lower returns due to the high demand and premium pricing of these bonds.
Interest Rate Risk: As with any fixed-income investment, rising interest rates can negatively impact bond prices.
Conclusion
On-the-run bonds are a vital component of the financial markets, offering high liquidity, efficient pricing, and benchmark status. These bonds play an essential role in shaping interest rates, influencing investment decisions, and supporting various trading strategies.
While they are a preferred choice for traders and institutional investors seeking liquidity and reliability, investors must weigh the trade-offs, such as lower yields and potential price fluctuations. Understanding the distinction between on-the-run and off-the-run bonds can help investors optimize their fixed-income portfolios based on their risk tolerance and investment goals.
Whether used for benchmarking, hedging, or short-term trading, on-the-run bonds remain an indispensable tool in the global financial landscape.





