Highlights:
- Definition and Purpose: A hedge wrapper is an options strategy used by investors with a long position in a stock, involving the purchase of an out-of-the-money (OTM) put and the sale of an out-of-the-money call to create a defined price range for selling the stock at expiration.
- Risk Management and Profitability: This strategy provides downside protection while limiting potential gains. The put acts as insurance against losses, while the call caps profits in exchange for a premium received.
- Applications and Considerations: Hedge wrappers are widely used in portfolio protection and strategic selling. However, they require careful selection of strike prices and expiration dates to align with investment goals.
Introduction to Hedge Wrappers
A hedge wrapper is an options strategy designed for investors who hold a long position in a stock but want to protect against downside risk while generating income. It involves:
- Buying an out-of-the-money (OTM) put to set a minimum selling price for the stock.
- Selling an out-of-the-money (OTM) call to collect a premium, which partially offsets the cost of the put.
This strategy creates a defined price range where the stock will be sold at expiration, depending on its market movement. It provides a balanced approach to risk management and income generation.
How a Hedge Wrapper Works
To illustrate, let’s consider an investor who owns 100 shares of a stock trading at $50 and wants to hedge their position. They implement a hedge wrapper by:
Buying a put option with a strike price of $45 (out-of-the-money). This ensures the investor can sell the stock for at least $45 if prices fall below that level.
Selling a call option with a strike price of $55 (out-of-the-money). If the stock rises above $55, the investor must sell at that price.
Key Outcomes of a Hedge Wrapper Strategy
- If the stock price drops below $45 → The put option ensures the investor can sell at $45, limiting losses.
- If the stock price rises above $55 → The call option is exercised, requiring the investor to sell at $55, capping gains.
- If the stock stays between $45 and $55 → The put and call expire worthless, and the investor keeps their shares while benefiting from the premium received from selling the call.
Benefits of Using a Hedge Wrapper
- Downside Protection Without High Costs
- The OTM put option acts as insurance, ensuring the investor does not face unlimited losses.
- The cost of the put is offset by the premium received from selling the call, making the hedge wrapper a cost-effective strategy.
- Income Generation from the Call Option
- By selling an OTM call, the investor collects a premium, which can:
- Offset the cost of the put.
- Generate additional income if the stock remains stable.
- Strategic Selling with Defined Exit Points
- This strategy predefines a price range at which the investor will sell the stock, helping in portfolio rebalancing and disciplined exit strategies.
Limitations and Risks of a Hedge Wrapper
- Limited Profit Potential
- If the stock price surges past the call’s strike price, the investor misses out on further gains beyond that level.
- This makes it less favorable for investors expecting significant upside potential.
- Obligation to Sell If the Call Is Exercised
- If the stock rises above the call strike price, the investor must sell their shares at that price, even if they prefer to hold.
- Timing and Strike Price Selection Are Crucial
- Choosing the wrong strike prices or expiration dates can lead to suboptimal returns or unnecessary limitations on profits.
When to Use a Hedge Wrapper?
When an investor wants protection against a moderate price decline but does not expect a significant rally.
When the investor is willing to sell the stock at a predefined range rather than holding for potential long-term appreciation.
When markets are uncertain, and the investor wants a hedge while earning premium income.
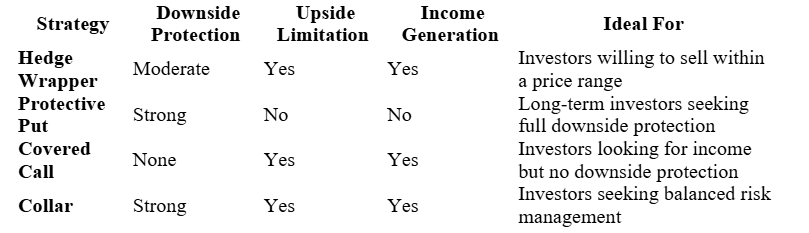
Comparison: Hedge Wrapper vs. Other Hedging Strategies
Conclusion
A hedge wrapper is a strategic options approach that balances downside protection with income generation, making it an attractive tool for investors with moderate risk tolerance. By defining a price range for selling stock, it allows for controlled risk exposure while ensuring a structured exit strategy.
However, it requires careful selection of strike prices and expiration dates to align with market expectations. While it limits profits, it provides security in volatile markets, making it a valuable addition to an investor’s risk management toolkit.