Definition
Related Definitions
Trading halt
A trading halt, also known as a stock halt, refers to a temporary suspension or a short-term trading stoppage of any security from being traded in a particular stock market, especially when a piece of news pertaining to that security is about to be broadcasted.
Generally, a trading halt is levied for regulatory reasons when a significant announcement is anticipated or to discourage price volatility related to a specific stock.

Summary
- A trading halt is a temporary suspension of a company's securities in anticipation of any significant news.
- These halts may be placed due to many reasons, like, major news related to a specific stock that is about to be released, to correct the imbalance between buy and sell orders or due to certain regulatory issues.
- The trading halt triggers stock prices, though it is not necessary that every halt will result in downward stock price movement.
Frequently Asked Questions
What are the possible causes for a trading halt?
Some of the common reasons due to which a trading halt occurs are as following.
- A significant piece of news about a company's products or business operations, whether positive or negative.
- Major corporate proceedings like mergers, acquisitions, and restructuring, etc.
- Certain regulatory proceedings.
- Occurrence of technical glitch/errors in a stock exchange.
- Major price gains or declines.
- Any development on the financial health of the company.
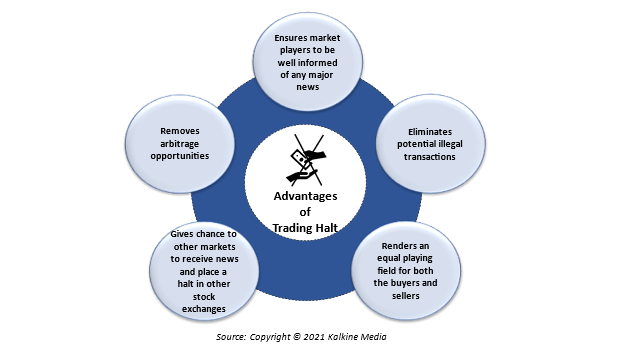
What are the advantages of a trading halt?
Generally, when trading halts are placed, investors get anxious. However, these halts, in fact, protect the interests of investors.
The below illustration shows some of the advantages of the trading halt on securities:
What are different types of trading halt?
There are two types of trading halt:
- Regulatory halt
- Non-regulatory halt
Regulatory trading halt occurs when a company has a significant pending announcement that may impact its share prices, thereby giving enough time to market participants to gauge the impact of such news. Another type of regulatory halt is when there is uncertainty over the company's securities, whether it meets the listing standards or not.
On the other hand, a non-regulatory trading halt happens when there is a considerable amount of imbalance between the demand and supply of a particular security.
What is the duration of a trading halt?
A trading halt has no ceiling. Generally, it lasts for few minutes to 1-2 days if the cause for the same is not very serious. However, if the trading halt exceeds 10 days, it is known as trading suspension. In such cases, investors whose funds get trapped as a result of the halt will have to wait till the halt is over.
What are the different trading halt codes?
Below is a list of some of the common trading halt codes, which indicates the reason as to why the security has been halted:

Source: Copyright © 2021 Kalkine Media
What is trade resumption?
The resumption or reactivation of the trading of securities after the halt is known as 'trade resumption.' It occurs after the end of the suspension of the companies' securities.
How do the NZX-listed companies apply for a trading halt?
Any company which is listed on the NZX and wishes to seek a trading halt must send a request to the NZ RegCo's Issuer Compliance team citing the relevant reason, duration, etc., in the prescribed template.
On receipt of the application, the authority considers the application and may ask for additional information. If satisfied, it gives its confirmation for the trading halt.
Does trading halt impact the stock price?
When the securities of a company are placed under a trading halt, there can be two possible outcomes; the stock price may either go up or may experience a decline once the halt comes to an end.
Therefore, when a trading halt of a specific security occurs, investors must examine the reason behind it. Share prices are likely to rise if there are changes within the company, and investors would benefit after the trade resumption.
However, in case of some major issues like illegal trading or fraud detection within a company, the trading halt may have an adverse effect on the stock price.
Can investors buy stocks during a trading halt?
When any stock exchange places a trading halt on any specific security, investors, traders, and brokers, etc., are unable to buy or sell that particular security. Trading can be resumed once the halt is over.
What should investors do when a security is hit by a halt?
A trading halt creates uncertainty and insecurity among investors and traders. In such situations, they must patiently take a closer look at the possible reason for the suspension of the stock's trading and work out ways for the next course of action once the halt is over.
Though not a welcome situation, stock price can, sometimes, see a climb after the end of the trading halt.
Some examples of a stock trading halt:
On 15 February 2021, NZ RegCo placed a trading halt on the shares of Contact Energy Limited as it undertook a capital raise. On the successful raising of equity worth NZ$325 million and the subsequent announcement by the Company, the trading halt was lifted on 16 February 2021 and CEN resumed trading its shares.
Tilt Renewables Limited sought a trading halt on 15 April 2021 for a pending announcement related to a superior scheme of arrangement for shareholders, which was lifted on 19 April 2021 and resumption of trading began thereafter.
- Salt Lake Potash Limited (ASX:SO4)
ASX levied a trading halt on the Salt Lake Potash Limited on 21 May 2021 because of the latter’s pending capital release. Normal trading of its shares was to re-commence by 25 May 2021 or after the released news.
