Definition
Related Definitions
Superannuation
What is superannuation?
Superannuation is a pension program created by an organization for the benefit of its workforce after retirement. It is a type of investment spread over the long term. In a superannuation fund, the employer contributes a fixed amount regularly as specified by the Superannuation Guarantee Legislation.
The employer’s contributions into the superannuation fund must be equal to at least 9.5% of the employee’s salary (known as Superannuation Guarantee). The employer may also contribute to the fund, and certain eligible employers may also benefit from co-contributions from the government.
This long-term investment is maintained till retirement and can be used by individuals if they do not have a fixed source of income to rely on.
The money put into a super fund is invested for further profits. Superannuation decreases the government costs of providing a pension to the retirees. Thus, one can get tax benefits on a superannuation fund.
How does a superannuation fund work?
The contributions to super funds are made by the employer and can be made by the employee as well. These are called ‘super contributions’. Both these contributions are invested in different assets.
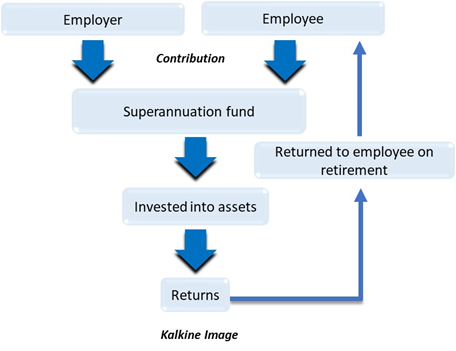
These investments can include anything from cash to fixed interest that offer annual returns which help grow your balance. The super funds can be accessed post the age of 65 or after the employee has retired. They can also be accessed earlier under special circumstances such as the case of a disability or a case of an urgent need of a large amount of funds.
Most superannuation funds can be managed by the employees themselves or by a third-party expert. When the employees choose to set up their own savings fund, it is known as self-managed super funds or SMSF. An employer can open an SMSF with up to three other employees and can manage these funds alone.
In case an employee changes a company, he or she can simply transfer the superannuation fund onto the new employer.
Who regulates the super funds?
Five authorities manage super funds in Australia. These include:
- Australian Securities and Investments Commission: The ASIC protects the consumers’ rights in all types of investments and securities, including superannuation. Under the Corporations Act of 2001, the superannuation trustees must maintain transparency about the super funds with the contributors.
- The Superannuation Complaints Tribunal (SCT): This offers easier access to dispute resolution than going to a court for the same.
- The Australian Taxation Office: This is an essential body, especially for the self manages funds. The ATO must ensure that the SMSFs comply with all the rules and regulations and are taxed appropriately.
- The Australian Prudential Regulation Authority: This body manages funds other than the SMSFs and ensures that proper compliance of rules and regulations is done.
- The Department of Human Services: The DHS must manage the requests of early liquidation of superannuation funds under certain specified conditions. This may happen when the fund member is in urgent need of money or is going through a health condition which disables them.
How many types of super funds are there?
Super funds can be of two types, which are:
- Accumulation Funds: In this type of a fund, the money grows or “accumulates” over time. The value of these super funds depends on the super contributions made by the employer and the employee and the investment generated the fund.
- Defined Benefit Funds: In this type of a fund, the return is calculated using an existing formula rather than being based on an investment return. These are mostly corporate of public sector funds.
What categories of superfunds are available to individuals?
Super funds can belong to retail, industry, corporate funds, or self-managed funds.
- Retail super funds are usually run by banks or investment companies. These have no restrictions on individuals and are open for contributions from anyone. They offer many investment options to choose from.
- Corporate funds are special funds created by employers for their employees. These may be operated under a board of trustees or by a retail or industry fund. These are not open to everyone, and only company employees can contribute to it. Unlike retail funds, all returns from these funds are returned to the members.
- Industry funds are curated to fit the requirements of people working in a particular industry or sector. However, anyone can join the bigger industry funds. Most of the industry funds are accumulation funds and are not-for-profit funds. This means that the benefits from these funds are put back into the funds.
- Self-managed funds are the funds that involve members investing the money into their fund. It has risks associated with it as the entire fund is to be managed by the members. It is a time-consuming task and may take up a lot of money.
What are the tax benefits offered under superannuation funds?
Superannuation funds are lightly taxed, which give them an edge over other forms of retirement benefits. This means greater returns post retirement than the returns earned from other retirement schemes available.
The before-tax contributions are taxed at 15% if the annual income of the employee is under $300,000. The contributions made with after tax money are not taxed. Also, the returns from an investment of super funds are taxed at 15%, if the annual income is under $300,000, and at 30% otherwise.
The benefits from superannuation can be received in a lump sum amount or through a fixed stream of income depending on the contributor.
The knowledge of superannuation amount upfront can help member take full advantage of the funds by planning out retirement in a better way.
How is a superannuation fund different from a pension fund?
A superfund and pension fund are very much alike. A pension fund can be considered an example of a defined benefit fund, which is a type of superannuation fund. However, the fundamental difference between the two is that super funds are maintained while an individual is employed while a retirement fund is only meaningful post retirement.
Thus, a pension is established by a retired individual by transferring some, or all, his money into it upon reaching preservation age. In comparison, a super fund is a long-term investment made when the individual is still employed.
The benefits from a pension fund are paid in the form of a fixed stream of income. They are taxed at the same rate as super funds, which is 15%.
GOOD READ:
