Definition
Related Definitions
Quick Assets
What are Quick Assets?
Quick assets refer to the assets that can be covert into cash within a short period. These assets defined as the liquid assets owned by a company such as cash and cash equivalent, accounts receivable and marketable securities.

Source: Copyright © 2021 Kalkine Media
Understanding Quick Assets
Quick assets include those assets which can be convertible in less than a year. These assets are known as the liquid assets of a company. Quick assets are used to calculate different financial ratios of a company that helps to understand the financial health of a company. Quick assets are a part of current assets along with inventories. Quick assets can be calculated by subtracting the inventories and pre-paid expenses from the current assets. Inventory of a company is not treated as quick assets as it takes more than a year to convert into cash. Companies use quick assets to meet their short term operating, investing, or financing needs.
For instance, Balance sheet of XYZ Company shows the following information, Current assets of £300000, Inventory of £80000 and pre-paid expenses of £50000. Here, we calculate quick assets by using the given formula:

Source: Copyright © 2021 Kalkine Media
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
What are the advantages of quick assets?
Advantages of quick assets are:

Source: Copyright © 2021 Kalkine Media
- Highly liquid: Quick assets are highly liquid. Therefore, companies use them for meeting their short-term operating requirements and financial needs.
- Source of finance: Quick assets works as a source of finance for a company, it helps in making new investments without going for credit.
- Helps in decision making: Quick assets highlight the financial health of a company that helps an investor in taking investment calls.
- Less risky: Quick assets are less risky than the non-liquid assets as they are easily and convertible in cash.
How do we calculate and interpret Quick asset ratio?
Quick asset ratio represents a company’s financial position to meet its short obligations by utilising its liquid assets. It indicates a company’s ability to use its liquid assets to meet its current liabilities.
It is commonly known as acid test. Quick ratio can be calculated by using the following given formulas:
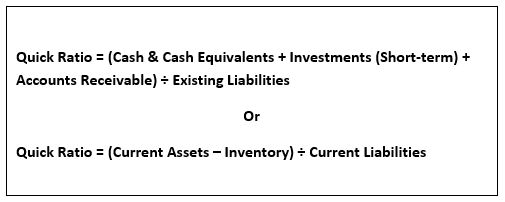
Source: Copyright © 2021 Kalkine Media
If a company’s quick ratio is equals to 1 that mean the company’s quick assets are equals to its current liabilities. If the ratio is higher than 1, it means the company’s quick assets are more than enough to meet its liabilities. The high quick ratio shows that a company utilises its short-term assets effectively to cover its financial needs and capable of settle its current liabilities, a company with high quick ratio left with cash or cash equivalents even after paying its current liabilities.
If quick ratio is less than 1, it means a company is not capable to meet its current liabilities with quick assets; a company has to tap into its long-term assets for paying its short-term obligations.
What are the disadvantages of Quick assets?
Disadvantages of quick assets are as follow:

Source: Copyright © 2021 Kalkine Media
- Loss of Opportunity cost: Sometimes holding more quick assets lead loss of opportunity cost for a company as sometimes quick assets do not earn any interest or each very less interest.
- Effect on Goodwill: A company’s high level of quick assets effect the goodwill of a company in investor’s eye as it indicates the company is risk-averse and not involved in investing into new ventures.
- Increase tax liabilities: Holding too much quick assets may increase the tax liability of a company as these assets are taxed in different way than non-liquid assets to promote investments.
What are the examples of Quick Assets?
Following assets are treated as the quickest (liquid) assets of a company:

Source: Copyright © 2021 Kalkine Media
- Cash: Cash refers to the physical money held a company at the bank. It also includes interest-bearing accounts such as deposits or recurring deposits.
- Accounts Receivable: Accounts receivable refers to the due balance of money for delivering goods or services. It is the amount which is yet to paid by customer to the company for its goods and services.
- Marketable Securities: Marketable securities refer to the financial investment securities that can be convert easily in cash by trading them in the secondary market in a reasonable price. It includes short-term investments such as bonds, stocks, and other securities investments.
What is the difference between quick assets and current assets?
Quick assets defined as a part of currents assets. Current assets include inventory and prepaid expenses along with liquid assets, but inventory and prepaid expenses are not a part of quick assets as they take time to convert. Quick asset provides the real picture of a company’s liquidity and ability to settle its short-term liabilities by utilising its short-term assets. In balance sheet of a company, quick assets are not shown as a separate head as it is a part of current assets.
Quick assets are more liquid in nature than the current assets, investors believe in quick ratio more than in current ratio as quick ratio treated as stringent test to know the liquidity of a company. Quick ratio of a company shows how effectively a company uses its short term assets to meet its short term obligations and liabilities including operating, investing and financial needs of company.
