Definition
Related Definitions
Private Equity
What is Private Equity?
Private Equity (PE) is generally defined as a direct investment in private companies rather than an investment in a public company in the form of buying shares. Investors directly obtain stakes in private firms or buy the whole company. Besides, investors may also buyout the public company, leading to its de-listing from the stock exchange.
Usually, Private Equity investment involves raising money from limited partners and further making investments (majority stakes) in the form of equity/ownership stake in mature businesses and established industries. Sometimes, PE investment also targets under-performing businesses with expectations of a turnaround.
The size, structure and nature of PE investment vary widely. The goal is to earn a decent Return on Investment (ROI) and eventually sell the stake at a higher profit.
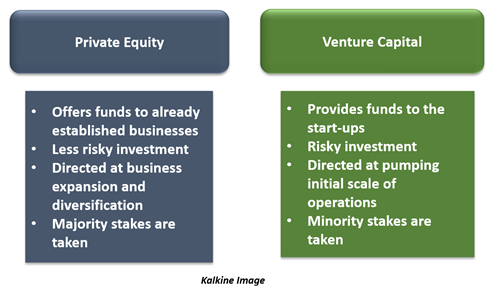
What is the difference between Private Equity and Venture Capital?
Similar to Venture Capital, Private Equity investment raises capital from limited partners that can be further invested in attractive companies with immense growth potential. However, there are some differences that deserve closer attention:
What is the Private Equity Investment Process?
The PE investment process consists of stages/steps involved while PE firms undertake key investment in businesses:
- Reviewing of the business plan: business evaluation in terms of management skillset, financial performance and expectation, return on equity and growth potential.
- Initial negotiation stage: analysis of financial structure (equity versus debt) and valuation, Offer Letter is sent out
- Thorough Due-Diligence: due-diligence from legal, tax and accounting perspective
- Final Negotiation: negotiation and contract signing stage
- Monitoring: post-investment monitoring of business prospects and performance
How are Private Equity Deals Funded?
The private equity funds are generally supported by several investors, including:
- Pension funds
- Insurance companies
- High net worth individuals
- Banks
PE firms raise capital from select few high-net-worth individuals and find the best possible business in an attractive industry with growth prospects to make the investment. These PE funds generally have a simple setup with a pool of research, tax, accounting and legal departments.
What is the Significance of Private Equity from Business Standpoint?
Wealthy investors pump capital into the PE funds for making investments that can be utilised for operational and diversification plans of the company such as undertaking a merger or an acquisition or investing in expanding the technology or launching a new product or services.
Private equity investment can strengthen the balance sheet of the company. Moreover, these funding options are advantageous in several ways as compared to conventional financing avenues.
These investments can be of varied nature, size and structure. Some investors offer funds to the underperforming companies to turnaround the businesses, while others invest in an exceptionally growing company. The level of involvement also differs depending on private equity funding.
When any PE firm offers funds in a targeted business, it expects to see the company grow according to the mutually agreed business plan. Working with the management team, the PE firm tries to improve business performance to achieve growth.
How does Private Equity Firms Make Money?
Businesses enhance their value with the investment coming from the investors in the form of PE funds. When the company is sold, PE fund and the investors earn the profit. When the company is underperforming, PE fund and investors lose money.
A private equity company often uses its own funds or borrows the funds to purchase the entity. During such transactions, PE companies need to leverage 60 to 70 per cent of the purchase price.
Private Equity is considered as an asset class, just like gold, silver, stocks, bonds. Investors put their money for greater return on equity instead of investing in other opportunities. PE, as an asset class, works best in exposure to other investment avenues.
Some of the known investment avenues of PE firms are:
- Hard assets such as real estate
- Infrastructures like ports or roads
- Sectors such as IoT, cloud computing, Pharmaceuticals, Automobile
What is the Significance of Private Equity from Investors’ Standpoint?
An investor always considers the two most important aspects while thinking of PE funds.
- A more comprehensive set of investment avenues for portfolio
- Benefits of diversification
Investors consider below drivers of return for investment at a portfolio level apart from the leverage effects.
- Growth: Consider investing $100 in a company with $50 revenue, and within three years, the company’s revenue has increased to $150. In that case, the value of $100 investment should now be $300. The investors focus on fast-growing companies while making PE investment.
- Margin expansion: Consider a company with $50 revenue and $5 as its profit, and the investor funds $100 to the company. After three years, the profit has become $15, but the revenue is constant. The company, therefore, is now 3x more profitable, increasing its PE investment value as well.
What types of PE funds exist, and how do they create value?
- The turnaround funds invest in distressed companies and try to fix them with the investment they made. Though this is the famous type of private equity funding, it is a small fraction of funds.
- The growth funds invest in new businesses which they expect to grow. The private equity team works with the company management to help them develop the business.
- Then there are sector funds focusing on specific sectors in which they have the experience to support the target company.
