Definition
Related Definitions
Net Income
What is net income?
Net income is the income a company earns from sales and other gains after the deduction of all expenses, interests and taxes for an accounting period.
The expenditures comprise selling, general and administrative expenses (also known as SG&A), cost of goods sold (COGS), depreciation and amortization (D&A), operating expenses, etc.
Net income is also called net profit and net earnings. As it is filed at the end of the company’s income statement, is also termed as the ‘bottom line’.
The formula for calculating net income is:

Copyright © 2021 Kalkine Media
Negative net income reflects the loss that a company has incurred in a given period of time, and it happens when the total expenses of the said company exceeds its total revenue.
Where does net income appear in the three financial statements?
Net income is an important accounting metric as it is a central line item in all three financial statements.
Although net income is derived from the income statement, it is also used in the firm’s cash flow statement as well as the balance sheet.
The cash flow statement is started with the net income or loss in the indirect method. Further additions and subtractions for non-cash revenue and expense items are done to find out the results of the operating activities’ cash flow.
In the company’s balance sheet, net income is reflected under retained earnings, impacting shareholder’s equity.
Why is net income important?
- To entrepreneur and management: Net income helps in assessing the health and success of a company, and in calculating the amount of tax it has to pay.
- To investors and shareholders: Net income is one of the most important metrics that investors generally look at before investing in the company. A part of the net income earned is also often distributed as dividends among the company’s shareholders. A healthy and consistent net income is expected to give investors and shareholders the confidence of getting a good return.
- To creditors: Banks, lenders and other financial institutions providing loans to businesses usually take a look at the net income, as it helps in evaluating the enterprise’s credibility.
Summary
- In accounting, the net income of a company is the income earned from sales and other gains after deducting the expenses, interests, and taxes.
- Net income can be negative as well.
- Net income gives a glance at the company’s profitability.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
- What distinguishes net income from operating income/operating profit
Operating income is the income a company generates from business operations after deducting variable and fixed operating expenses. It can be termed as operating profit as well.
In simpler terms, it is the profit a business earns from its core operations.
The formula to calculate operating income is:
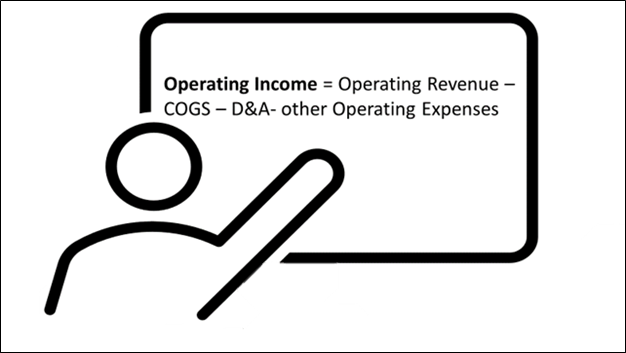
Copyright © 2021 Kalkine Media
Key differences:
- Operating income does not include interest on loans, taxes, debt payments and other one-time payments.
- Operating income includes only revenue generated from its business operation and does not add ‘other revenues’, such as interest earned on investments, in its calculations.
It is important to note that a company can earn huge profits from its operations but still report a net loss for the fiscal year. As a result, to evaluate the profitability, a company is suggested to evaluate each metric, such as gross profit, operating profit, EBITDA, etc. to understand the overall performance.
For instance:
Suppose a company earns US$ 80 million operating profit and includes a significant amount of debt in its balance sheet. The interest charged on this debt is US$ 100 million. In that case, the income statement shows the loss of US$ 20 million despite having an operating profit of US$ 80 million.
- Which financial ratios are directly impacted by net income?
The financial ratios which include net income as part of their calculations are:
- Net Profit Margin = Net Income / Revenue from operations
It is part of a profitability ratio providing the final picture of how a company performs after bearing all the expenses. One drawback of this ratio is that it includes a lot of ‘noise’, like one-time expenses and gains, making it difficult to compare.
- Return on equity = Net Income / Shareholder’s Equity
Or
Net Income/ (1 - Dividend Payout)
A high return on equity ratio shows a company is competent in generating cash internally. As a result, the company becomes less dependent on borrowings.
- Return on assets = Net Income / Average Assets
It is a profitability ratio, showing how well a company can generate profits from its assets.
- Is financial performance more closely related to the net income generated or to the cash flows of the company?
Net income reflects a business’ profitability, and a higher net income does not show high liquidity.
On the contrary, a company’s cash flow statement, which signifies its cash inflow and outflow, summarizes how it manages its cash position and funds its operations. Therefore, a company’s financial performance is more closely related to its cash flow than its net income.
- In what scenario an enterprise can have a negative net income along with a positive cash flow?
A company’s cash flow statement does not reflect its profitability. Its function is to show how much cash is being spent and earned in a particular accounting period by a company.
A few scenarios where a company can report a positive cash flow along with a negative net income is as follows:
- if the company has borrowed money, in which case the amount will be reflected as an inflow in the cash statement,
- if the company has borne a huge depreciation cost, which is subtracted while calculating net income. However, in the cash flow statement, the depreciation cost will be added back as it is not a real expense borne by the company.
