Definition
Related Definitions
Limited Liability
What is Limited Liability Company?
In the Limited Liability Company (LLC) business structure, the owners are termed as members, and they are not liable for the liabilities or debts of the organisation. LLC allows the members to distribute the income along with protection from the organisational debts. Moreover, the income of the members is shown as the salary to the employees and is deducted from the company’s expense account.
US State laws list the organisations which are not allowed to form LLC. In the majority of the states, banking institutions and insurance companies are not allowed to form LLC. Few states mention the services which LLC cannot perform. For example, California prohibits the services such as doctor’s clinics, pharmacies, law firms and accounting firms. Some state laws describe the number of members and who cannot be a member of an LLC. Few states prohibit LLCs with a single member.
Summary
- In Limited Liability Cooperation (LCC), the members are not liable for the liabilities or debts of the organisations.
- The state government governs LLC.
- State laws highlight the organisations which cannot be formed under LLC.
FREQUENTLY ASKED QUESTIONS (FAQS)
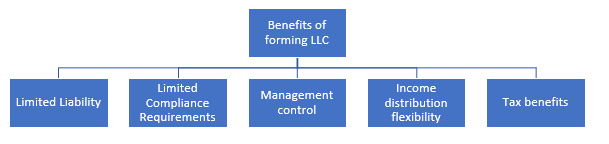
What are the Benefits of creating LLC?
Source: Copyright © 2021 Kalkine Media Pty Ltd
LLC extends the benefits to both Corporation and partnership firm.
- 1. Limited Liability - The members of LLC are shielded against the personal liability of the Company formed. The collectors cannot include the personal assets of the members in order to pay their debts as members and organisations are seen as separate legal entities. In few cases, the assets of the members can be used for paying debts as per the state law.
- Compliance Requirements – The legal requirements for forming an LLC are easy in comparison to the partnership, praetorship, or Corporation. Similarly, LLCs are subject to limited compliance requirements, which further reduces the cost.
- Tax benefits – The Company does not pay tax at the entity level, but the taxes are paid based on the income of the members. This extends the protection from double taxes, i.e., taxes firstly paid by the Company and by the owners on their income.
- 4. Income distribution flexibility – The members of the LLC have the freedom to distribute the income in different ratios. For example, all the members have contributed the same capital, but two members have devoted more time and will be given more income on that basis. The LLC does not bind the members to distribute income in a specific ratio.
- Management – In Company, the management control lies in the hands of the board of directors. However, it is not true in the case of an LLC. Members have the authority to formulate a group and take control of the management directly.
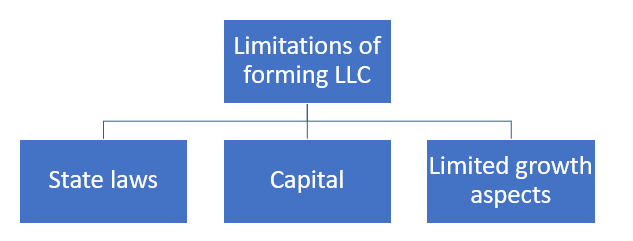
What are the Disadvantages of LLC?
Source: Copyright © 2021 Kalkine Media Pty Ltd
- State Tax – Since the LLCs are governed by the state government, they are subject to annual taxes in the form of annual fee or state tax.
- Capital – LLC can either raise capital from equity or debt. In raising the money from equity, members must sell the ownership of the organisation, increasing to members. Afterwards, the income must be distributed among the members. Furthermore, managerial power will be lost. Since the popularity and trust component are missing in LLC, finding a potential investor will be a challenge. Creating capital by the medium of bank loans is a challenge as there is a limit in terms of the loan provided to LLC.
- Limited growth aspects – the state governs the registration and compliance requirements of LLC. So, when LLC expands their operations across states, they face the challenge of adopting different state laws. This limits the growth or expansion opportunity of LLC.
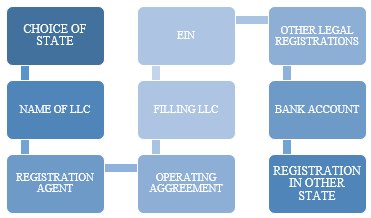
What are the Steps to form LLC?
Step 1: Choice of state – The majority of the members chose the state where they live, but members can choose other states as well. LLC can select a state and choose not to perform their operations in that state. The choice is generally dependent upon the cost of administration, fees, taxes, and formation.
Step 2: Name of LLC- The name of the organisations will be dependent upon the state’s record of businesses conducted within the state. To avoid legal complications, the availability of the name LLC has to be ensured. Even if the registration is not planned in the near future, then the title should be reserved. With a small fee, the name can be registered with the state government.
Step 3: Registration agent- At the time of registration, a registration agent should be appointed. The role of the agent includes managing the tax documents, receiving and managing the legal documents, and maintaining communication with the government. The member can perform the role of registration agent, but the LLC can face issues in case of unavailability of the member.
Step4: Operating agreement- Agreement between the members and LLC can be oral or written. Agreements state that members and organisation have separate legal entities. Furthermore, it says the actions which will be undertaken in different circumstances.
Step 5: Filling LLC- To make the existence of LLC official, the following documents are needed to be submitted to the state’s office.
- Certification of organisation and formation that includes:
o Purpose, location, and name
o Registration agent’s details
Step 6: Employer Identification Number (EIN) - Employer identification number must be obtained from the internal revenue service department. EIN is crucial for bank account and tax filing.
Step 7: Other legal registrations- The identification number must be obtained from the tax department for filing sales tax. Furthermore, it is necessary to register with the state's labour department to safeguard the LLC from future legal issues.
Step 8: Bank Account- It is not a legal requirement, but it is suggested to open an account with the help of EIN. The bank account should be opened with the name of the organisation instead of the member’s name. Based on separate bank accounts, the liabilities of the organisations are paid off to the creditors.
Step 9: Business registration in other states- While expanding the business in the foreign states, the registration must be done in those states. For other states, the registered agent is often required along with documents of good standing.
Source: Copyright © 2021 Kalkine Media Pty Ltd
