Definition
Related Definitions
Junior Company
What is junior company?
A junior company engages in the development of natural resources, such as confirming resources at an exploration location, conducting research, and carrying out actual extraction, among other things. Apart from that, they all share the immediate risk of such exploratory activities failing.
Like any other startup, junior firm looks for a large corporation to buy it out or funding to help it grow. However, it is usually classified as a small-cap company because of its low market capitalisation and low trading volumes.
Junior enterprises typically acquire fixed assets with potential natural resources and mineral resources. Then, they carry out a study in the area to see whether there are any possible minerals or resources.
The study findings are provided to the public or stockholders as proof of the natural resource's existence. If the research is successful, the junior business will seek funds to continue its exploration or will strive to be acquired by a giant corporation.
Summary
- A junior company is a brand-new firm formed to develop a natural resource deposit or field.
- Junior companies strive to expand by receiving capital or by being acquired by a giant corporation.
- Junior companies carry a high level of risk because they are new to the market and have not yet established their asset base.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
What is company?
A company is a corporate body formed by a group of professionals to engage in and manage a business, industrial or commercial venture. A business could be constituted in a variety of ways for financial liability and tax reasons, depending on the jurisdiction's corporate and commercial law.
The company's line of business will greatly influence whether it prefers a corporation, proprietorship, or partnership as an organisational structure. These structures also symbolise the company's ownership structure.

Source: © Stnazkul | Megapixl.com
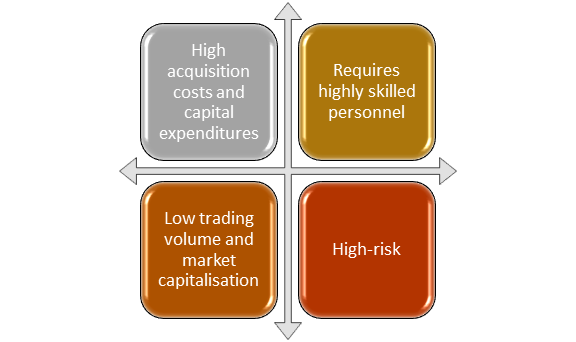
What attributes define junior company?
High acquisition costs and capital expenditures
Because their project necessitates a significant amount of excavation activities, and development technologies, research, and machinery can be expensive, junior enterprises tend to have substantial capital expenditure. As a result, businesses prefer to invest heavily in fixed assets.
Furthermore, junior firms have high acquisition costs since they must initially buy sites with prospective resource deposits before doing resource studies and exploration.
Low trading volume and market capitalisation
Junior companies often have a market capitalisation of less than $1 billion and are thus classified as "small-cap corporations." Furthermore, such organisations typically have minimal trading volumes, resulting in daily trade volumes that are essentially non-existent or extremely low.
Requires highly skilled personnel
Junior industries recruit a team of highly skilled technical professionals and management personnel to oversee the firm and its projects, as well as to ensure that the company is in good standing and following local government norms and regulations.
High-risk
Junior enterprises are regarded as "high-risk" since their success is dependent on the study carried out to determine the presence of a mineral or natural resource. A negative result from research would eliminate the potential of receiving additional funding for exploration, and the cash invested on studies and site purchase would become a sunk cost.
Source: Copyright © 2021 Kalkine Media
Who prefers to invest in junior companies?
Investing in junior companies carries a higher risk than investing in established and larger companies because juniors are still researching and may not uncover any resources at all.
Investors that are interested in smaller, up-and-coming businesses should diversify their portfolios to decrease risk and maximise returns.
Individual investors are more likely to be interested in juniors since they typically make decisions based on their emotions.
Hedge funds and mutual funds, for example, will typically invest in mature companies with a longer track record.
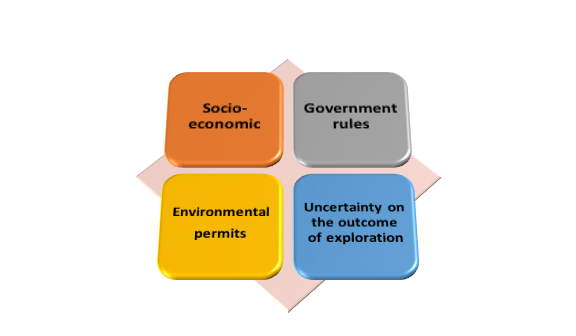
What are most prevalent problems that junior company faces?
A junior company is a small business that relies exclusively on natural resource exploration, development, and research. The issues that a junior company may confront while functioning is listed below.
Government rules and regulations
Junior corporations may find that the properties they've discovered and want to buy are on tribal territories, necessitating the relocation or rehabilitation of indigenous residents.
Difficulties in finding environmental permits
Due to limited regulations or practices, junior firms may have difficulties finding environmental licences in certain nations or states where an indicated exploration site exists. In addition, due to a lack of weak liberal policies or political interest, some governments may be unwilling to provide environmental licences. Companies may also be exposed to dangers linked with the potential country, such as a raging civil war.
Uncertainty about the outcome of exploration and research
Junior firms may be in danger of failure since they must initially acquire land before starting exploration or research. The outcomes of their research will establish whether or not a natural resource exists. If the study results are wrong, the funds invested in research and acquisition would be lost. As a result, failures can sometimes lead to the junior company's insolvency, especially if its borrowing is very high.
Socio-economic
In most African countries, such businesses must form a joint venture with a local community or corporation because the resources found on these communities' lands also belong to them. For example, the Blue Rock Diamonds group was formed in the UK and works in South Africa in collaboration with Ghaap Mining (Pty)Ltd, Kimberly, that controls 26% of the company's capital structure. Again, it's due to the Black economic empowerment regulations' obligations.
Source: Copyright © 2021 Kalkine Media
What is example of junior corporation?
One example of a junior mining firm is Kincora Copper Ltd. (ASX: KCC). As of 6 June 2021, the company has a market cap of $35.61 million and a daily trading volume of approximately 128,890, firmly placing it inside the small-cap category.
Kincora Copper is a project generator and active explorer focused on world-class copper-gold finds. The company is currently drilling the brownfield project.
