Definition
Related Definitions
Joint stock company
What is the concept of a joint stock company?
A joint stock company is a type of business wherein shareholders are considered the company's owners and have the right to buy and sell stock.
In joint stock companies, the owners are expected to share profits, and they are formed to finance ventures that are too costly for an investor or even a government to invest in.

Source © Terovesalainen | Megapixl.com
Summary
- A joint stock company is one in which all its owners own a portion of the company.
- A joint stock company combines the arrangement of a corporation with the autonomy and flexibility of a partnership.
- Joint-stock company shareholders have unlimited liability.
Frequently Asked Questions
What role does a joint stock company play?
A joint stock company is a legal arrangement between entities that creates a new organisation for commercial purposes, allowing two or more shareholders to form a corporation.
A joint stock company's shares are transferable. The shares of a public joint stock company are traded on licenced stock exchanges and they can be transferred between individuals, but this is usually restricted to family members by consent.
Shareholders of joint stock companies have unlimited liability, which means they are collectively responsible for all of the company's debts and financial obligations, and their assets can be seized to pay for unfulfilled financial commitments and debts if the business fails.
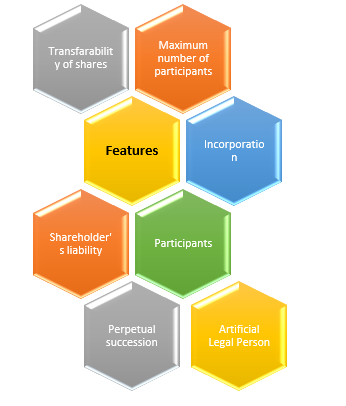
What are the key attributes of a joint stock company?
Artificial Legal Person
A corporation is a legal organisation formed by statutes of law. It also has some legal protections, which it exercises through its board of directors.
Though, a corporation is not subject to all rules, privileges, or obligations. It only occurs in statute, not in any physical form. So, it is referred to as an artificial legal person. The organization's day-to-day activities are overseen by the board of directors.
Maximum number of participants
According to the Companies Act, a joint stock company must have a maximum of 50 shareholders and a minimum of two shareholders.
A separate legal entity
Unlike a sole proprietorship or partnership, a corporation's legal identity and that of its members are distinct. As soon as a joint stock company is formed, it receives its legal identity. As a result, a business member is not responsible for the company. In the same way, the corporation would not depend on any of its members to conduct business.
The company's incorporation
A corporation must be organised to be recognised as a separate legal entity and to come into existence. A business does not exist until it is incorporated.
Perpetual Succession
The joint stock corporation is the outcome of the absence of the law. The life of a company is unrelated to the activities of its members, they change over time, but this has little bearing on the company's life.
The shareholder’s liability
The difference between a partnership, a sole proprietorship, and a joint stock company is represented by the shareholder's liability. Because a shareholder's liability is limited, the assets of the company's members cannot be liquidated to pay the company's debt.
Transferable shares
Shares can be transferable in a joint stock company. People can face limitations when exchanging their shares, but transactions in public corporations cannot be prevented.
Source: Copyright © 2021 Kalkine Media
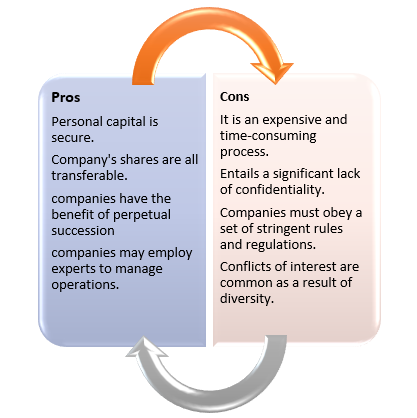
What are the benefits of forming a joint stock company?
- The liability of a joint stock partnership is limited to the unpaid balance on the member's shares. Their capital is secure in this situation, and they are welcomed to invest in joint stock companies.
- In a joint stock company, shares may be transferred.
- Since the shares of a joint stock company can be passed on from generation to generation, they have the advantage of eternal succession.
- Since all operations are overseen by a board of directors, most joint stock companies are extremely well controlled.
- Due to their vast resources, joint stock companies may employ experts to manage their operations.
- An organisation employs a board of directors to oversee all operations, and competent, talented individuals are elected to the board, resulting in effective and productive management.
What are the disadvantages of forming a joint stock company?
- Creating a joint stock corporation is an expensive and time-consuming process that requires a significant amount of time and energy.
- Running a joint stock corporation entails a significant lack of confidentiality, as the Companies Act requires all public companies to make their financial statements public.
- Joint stock companies must obey a set of stringent rules and regulations, greatly limiting their rights. As a result, joint stock companies' activities are limited.
- There are several different types of owners in a joint stock company, from shareholders to promoters and debenture holders.
Source: Copyright © 2021 Kalkine Media
