Definition
Related Definitions
index
What is the index?
A stock market index tracks the stock market and changes in the share prices of various firms. It is a method used by financial firms and investors to assess the return on particular investments and to define the market. It is calculated by comparing the stock prices.
Summary
- Market indices are groups of stocks that are intended to track the output of a specific market sector.
- Investors may use indices to invest passively or as a benchmark against which to measure the performance of their portfolio.
- It is a metric that represents a segment of the stock exchange and calculated by comparing the prices of various stocks.
Frequently Asked Questions
What is the significance of stock market index?
Indices are used by economists and investors to monitor market performance and stock price movement.
Indices are extremely useful in the financial world for monitoring items like publicly traded stocks, bonds, and consumer prices for popular commodities. Over 3 million different indices have been designed as of 2020 to essentially control every specific niche of the market.
The daily results of stock indices are probably the most well-known and significant figures in finance and investing. The Dow Jones Industrial Average (DJIA), which is perhaps the most famous and commonly used stock market index in the world, is made up of the top 30 publicly traded companies in the United States.
Investors' investment portfolios and the capital markets are controlled by market indices.
They also offer a wealth of knowledge to investors, assisting them in developing and implementing investment strategies.
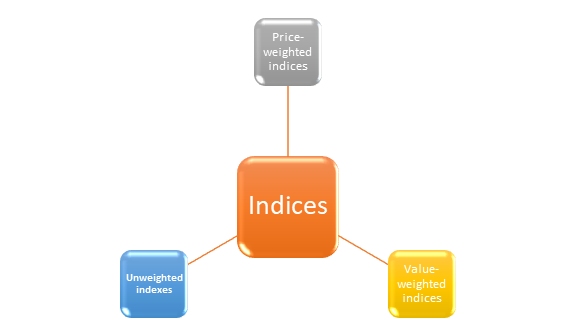
What are the various ways of weighting indices?
Indices are intended to monitor the performance of stocks in the market. To comprehend the results, it is necessary to understand how each index is weighted. The weighting of an index has a significant impact on its performance. Stocks with more weight in a weighted index will have a greater impact, whereas no single stock in an unweighted index has more weight.
There are several ways for weighting indices, but the following are the most common:
- Price-weighted indices: The share price of each stock in the index determines its proportional share in the index.
- Value-weighted indices- The proportional share of each stock is determined by its total market capitalisation.
- Unweighted indexes- Within the index as a whole, each stock has the same value.
Source: Copyright © 2021 Kalkine Media
What are the purposes of indices in mutual funds and ETFs ?
Indices offer investors, traders, and buyers a wide picture of market performance. Exchange-traded funds (ETFs) and mutual funds often use indices as performance indicators.
The term "indexing" refers to a type of passive fund management. A fund portfolio manager creates a portfolio that matches the securities of a particular index, rather than stock picking and market timing (that is, determining which securities to buy and when to purchase and sell them).
Index funds were designed to monitor the performance of indices and no one can invest directly in them. These funds have securities that closely resemble those found in an index, enabling investors to wager on the index's results in exchange for a fee.
Fund sponsors try to build portfolios that mimic the elements of a specific index when bringing together mutual funds and ETFs. This enables the investors to purchase a security that will fluctuate in lockstep with the stock market as a whole or a part of it.
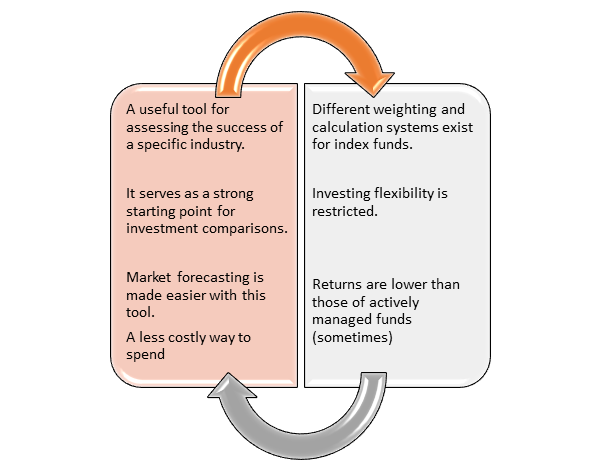
What are the benefits of stock indices?
An index is a valuable instrument for evaluating a market's success and offering a reasonably reliable assessment of how the sector is gradually progressing.
The index is a good starting point when comparing investments, and a portfolio can be compared to one to see if it is progressing as predicted.
Economists and investors can use past data to predict how different indexes will react to specific market forces in the future. Index funds have lower costs because they track their market index actively.
What are the drawbacks of stock indices?
Because of the various weighting techniques, it can be difficult to predict how different indices would behave.
There is a lack of investment versatility. If you invest in index funds, you are locked into the performance of the specific index and are unable to make changes as you see fit.
Source: Copyright © 2021 Kalkine Media
What are some leading stock indices to look at?
1. The ASX 200 – Australia’s S&P 500
The ASX 200 is the most commonly used index for measuring overall industry performance.
Many large-cap firms, such as BHP ($102 billion) and Commonwealth Bank ($140 billion), are included in the ASX 200, as are smaller but still well-known companies, such as Bega Cheese ($955 million) and Speedcast Int ($240 million) .
2. The S&P/ASX 200 financials
This index gives investors a glimpse of Australia's ever-important financial market.
Under the S&P/ASX 200 financials index, here is a snapshot of the company's operations:

Source: Copyright © 2021 Kalkine Media Pty Ltd
- S&P/ASX 200 materials
The S&P/ASX 200 materials index includes a diverse group of commodity-related manufacturing companies. Glass, chemicals, forest products, building materials, paper, and related packaging products, as well as minerals, metals and mining firms, including steel manufacturers, are all included in this market.
