Definition
Related Definitions
Geothermal Energy
What is Geothermal Energy?
Geothermal Energy is a form of renewable energy that is derived from the subsurface of earth. The energy is carried to the surface with the help of water or steam. Geothermal energy can be used in various applications ranging from home heating purposes to industrial purposes depending on the characteristics, location of origin and intensity of heat. The heat energy contained in the subsurface rocks comes from the molten magma of the earth.

Geothermal Field Namaskard, Iceland, Image Source: © Hel080808 | Megapixl.com
What is the source of Geothermal Energy?
To understand the source of geothermal energy, we must first understand the earth's basic structure. The earth consists of four major layers, including the inner core, outer core, mantle and crust. Let us try to understand the composition and thickness of each layer and how they contribute to the formation of geothermal energy.
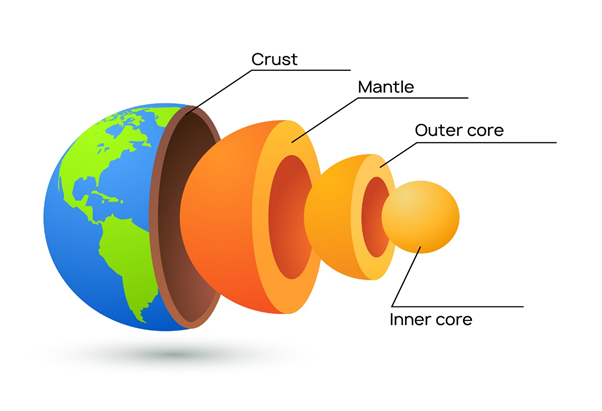
Source: © Vasilyrosca | Megapixl.com
- Inner Core: The inner core of the earth is a solid iron ball with a diameter of about 1,500 miles. The temperature of the earth's inner core lies around 10,800 degrees Fahrenheit, which is as hot as Sun's surface temperature.
- Outer Core: The outer core of earth is in a semi-solid state, containing hot molten rocks called magma. It is mainly composed of nickel and liquid iron, and the thickness of the outer core is about 1,500 miles. The temperature of the outer core lies between 8,132 to 9,932 degrees Fahrenheit.
- Mantle: Mantle is a layer of molten magma surrounded over the outer surface of the outer core. The thickness of the mantle is around 1,800 miles. The temperature of the mantle ranges from 7,230 degrees Fahrenheit at the core-mantle boundary and 392 degrees Fahrenheit at the crust-mantle boundary.
- Crust: Crust is the outermost surface of the earth which is made up of rocks. The solid rock masses present on the surface of earth contributes to the formation of the ocean and continental floors. The thickness of crust ranges from 15 to 35 miles in continents and 3 to 5 miles under the oceans.
The slow decay of radioactive particles inside the earth’s core produces heat energy. The heat energy is then carried out by semi-solid magma present in the outer core to the mantle and ultimately to the surface in the form of volcanoes through the edges of plate boundaries. Rocks and water sometimes absorb heat from this molten magma found underground. This heat energy is converted into usable form and termed as Geothermal Energy.
How is geothermal energy harnessed?
Wells are drilled up to the subsurface zones into underground reservoirs to bring hot water or steam to the surface. The steam or hot water can then be used to rotate turbines and in turn to generate electricity with the help of mechanical electricity generators.
There are three main types of geothermal plants, including Dry Steam, Flash and Binary, used to generate electricity.
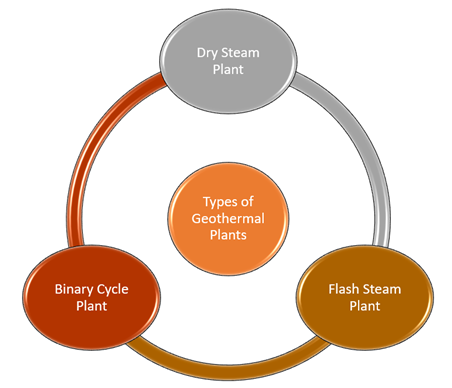
Copyright © 2021 Kalkine Media Pty Ltd
- Dry Steam: Dry Steam is the oldest and conventional form of geothermal plant which directly uses steam from the reservoir to run the turbines. The first geothermal plant was built in Italy in 1914.
- Flash Steam Plant: Flash Steam geothermal plants take high pressurized hot water from the reservoirs to convert it into steam to drive mechanical generators for producing electricity. As soon as the water gets cool, it is reinjected into the subsurface from the well to be used again.
- Binary Cycle Power Plants: Binary Cycle Power Plants use binary cycle to drive the generators. These plants are installed in areas where the intensity of heat is slightly lower. The heat energy of water from the underground reservoirs is first transferred to another liquid having a lower boiling point than water. The liquid is then used to generate steam and drive generators for electricity production.
Summary
- Geothermal Energy is a form of renewable energy that uses earth’s heat energy to drive the turbines and generate electricity.
- The decay of radioactive particles present inside the inner core produces heat energy which is transferred to the surface and harnessed for various purposes.
- There are three types of geothermal power plants used widely for the generation of electricity.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs):
What are the advantages and disadvantages of Geothermal Energy?
The biggest advantage of geothermal energy is that it is an eco-friendly source of energy. It is carbon-free energy and doesn't have any major ill effects on the environment. It is a renewable and sustainable form of energy that can provide an uninterrupted supply. Geothermal power plants produce a nominal amount of carbon dioxide emissions.
However, there are few drawbacks of using geothermal energy too. The production of geothermal energy involves hydrogen dioxide and sulphur dioxide emission, which is very harmful to the environment. The process to harness geothermal energy can induce mini tremors in the operational area. In addition to that, it is an expensive form of energy that required huge capital investment.
What are the different uses of geothermal energy?
Earth's heat energy is used as geothermal energy to perform various tasks. Some of the applications of geothermal energy require a well to be drilled, whereas; others use earth's surface temperature.
- Direct Use: Geothermal energy can be directly used for various purposes like bathing, heating buildings, food dehydration, mining, milk pasteurization etc. The hot water from the reservoirs or springs can be used for all the above-stated purposes, and it does not require any well to be drilled.
- Electricity Generation: The second most important application of geothermal energy is electricity generation. There are three types of geothermal power plants which are used widely for electricity generation. The power plants are installed near the geothermal reservoirs. The US is a leading producer of geothermal based electricity. Geothermal plants in seven states of the US produced 17 billion kWh electricity in 2020, as per EIA data.
- Geothermal Heat Pumps: Geothermal Heat Pumps are cost-effective and eco-friendly sources for maintaining the temperature of buildings including, schools, hospitals, offices, homes etc. The pumps use the earth surface's constant temperature to heat or cool the building. The pumps transfer heat from building to ground in summers and from ground to buildings in winters.
