Definition
Related Definitions
Freudian Motivation Theory
What is Freudian Motivation Theory?
Neurologist and psychoanalyst Sigmund Freud developed the Freudian theory of motivation. According to the theory, people’s choices are largely based on their unconscious behaviour. This means that people may seek motivation for buying certain goods through their unconscious channel of thinking.
Individuals may not always fully understand why they make certain choices, since these are driven by their unconscious behaviour and not necessarily by wants or needs. This theory is frequently used in understanding consumer behaviour and in analysing the purchasing patterns of individuals.
What are the components of Freudian motivation theory?
According to Freud, the human psyche has two different parts: the conscious mind and the unconscious mind. Both these include three components in total: id, ego and superego.
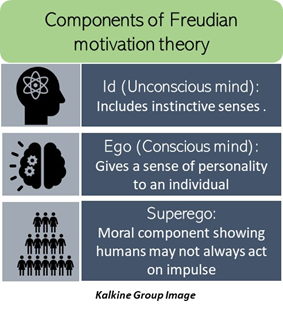
- Id: According to Sigmund Freud, the id is the biological component of every individual’s thought process. Id includes instinctive senses that everyone holds since birth. It is the unconscious mind.
- Ego: Ego represents the conscious mind, and it is made up of thoughts, memories, feelings that individuals may base their decisions on. The ego gives a sense of personality to an individual.
- Superego: This includes society’s perceptions regarding ethics, values, taboos, etc. It is the moral branch that can influence how humans make decisions. This component shows that humans may not always act on impulse and is the “inner-voice” or conscience of humans.
In some people id may be stronger; however, in others superego may be stronger. The relative strength of id, ego and superego determines how a human being takes decisions.
Why is the Freudian motivation theory important?
Freudian motivation theory can be applied in the fields of sales and marketing. The theory suggests that individuals may decide which products to buy based on their emotions and feelings, without consciously knowing it.
Consider the example of a man who buys a new car given the fact that his old car is in good working condition. It is possible that the man’s decision to purchase a car was motivated by his urge to create a status symbol for himself in society. This decision may not be as conscious as the buyer would think it to be.
To utilise the Freudian motivation theory's emotional standpoint, salespersons can incorporate specific marketing tactics that could trigger an emotional response from the customer, leading him to buy the product. Thus, motivation theory can help sellers achieve the desired response from the customers.
How is the Freudian motivation theory applied?
Corporations may reach out to motivation researchers who collect data from potential customers. The data is collected through interviews to understand the deeper motives behind buying a particular product.
These researchers may use various techniques like word association, picture interpretation, sentence completion, role-playing, etc to understand how individuals make decisions. This information can enable marketing researchers to decide how these unconscious motivations can be best exploited to make the product lucrative to individuals.
Freudian motivation theory states that the sale process has three parameters:
- Consumer satisfaction
- Functional needs satisfaction
- Unconscious needs
What are some other theories of motivation?
Apart from Freud’s theory of motivation, there are two other popular motivation theories. These include:
- Optimal-level Theory: This theory is also referred to as the theory of homeostasis, a term coined by French psychologist Claud Bernard. Homeostasis refers to the state of equilibrium in the body. This ideology belongs to the “hedonistic” theory, which states that happiness is the highest good.
According to the hedonistic theory, there is an optimal level of normal functioning in every individual, allowing him to make the right decisions. However, if the individual were to fluctuate from this position to disequilibrium, he would not find it pleasurable.
Thus, every human being strives to be in a state of equilibrium by maintaining an optimal level of needs like food, water, etc.
- Humanistic Theory: This theory believes in human beings' capacity to realise their own potential, strengthen their self-confidence, and achieve the ideal self. These can include biological factors like hunger, thirst; safety needs; love and belongingness need, esteem needs like respect and approval; self-actualisation motive like attaining maximum level of one’s capacities.
