Definition
Related Definitions
Fiduciary
Image Source: © Savkoand277 | Megapixl.com
What is meant by Fiduciary?
Fiduciary is a legal term that refers to an organisation or an individual that has been given the responsibility of acting on behalf of another person or entity. Some examples of fiduciaries include bankers, attorneys, and officers.
Fiduciaries are given the task of acting in the interest of the concerned individual. Any action taken by the fiduciary must be with complete integrity and honesty. If the fiduciary does not abide by this, then they are legally liable. Fiduciaries may also be financial advisors to their clients who invest on their behalf.
What sets a fiduciary apart from other advisors?
A fiduciary is better than an advisor as it promises to act in the client's best interest, including the financial interests. Any strategy recommended by the fiduciary must be the one they would go for themselves, had they been in the shoes of their client.
Any provisions provided to the fiduciary can be taken away if misused, and the fiduciary would be charged with legal action. A fiduciary is associated with lesser conflict of interest than other financial advisors and is expected to maintain a high transparency level.
How does an agreement with a fiduciary work?
Any agreement with a fiduciary involves the trustee and the beneficiary. The legal power that a fiduciary is entitled to includes access to the client’s money, property, or wellbeing of the beneficiary. A fiduciary’s actions should not break the trust of the client.
A fiduciary must not make decisions that are beneficial to himself and detrimental to the client. A fiduciary can not carry out additional expenses on behalf of the client. This includes hiring incompetent people who are not fit to carry out the expected task.
The deal is made official through a fiduciary agreement describing the relationship and responsibilities of the parties.
What types of fiduciary are there?
Fiduciary can be broadly divided into governmental and non-governmental forms. Other types of fiduciaries include:
- Lawyer: Lawyers have a fiduciary duty toward their clients. Lawyers should disclose any conflicts of interest and should focus on the best interest of their client. Fiduciary duties should be abided not just by individuals practicing law but even by large firms.
- Guardian: A guardian who has been legally obligated to look after a minor has to act as a fiduciary. Here, the client refers to the parent who has given caretaking rights to the guardian.
- Decision making board: Consider a company where the board of directors is responsible for managing all stakeholders' interests. As their decision immensely affects the company's shareholders and shareholders, the board must act as a fiduciary. Shareholders can be adversely affected if the board takes a wrong decision that benefits them at the shareholders' cost.
- Financial Advisor: Financial advisor handles an individual’s assets, funds, and all liquid holdings. This control over funds can easily be misused to act in favor of the advisor and not the client. Advisors may also sometimes have the rights to handle these funds without seeking the approval of the client. Thus, the role of the financial advisor is that of a fiduciary.
- Real Estate Agents: Real estate agents can be considered fiduciaries as they manage their clients' funds. Real estate agents can either be from the buyer side or seller side. The fiduciary arrangement can be arranged till the interests of both parties are fulfilled.
What duties must a fiduciary fulfil?
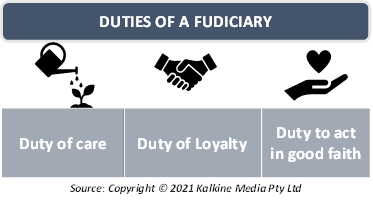
Fiduciaries must fulfil two main duties: the duty of care and the duty of loyalty. However, there may be times when more is expected out of fiduciaries, depending on the type of client. These two duties are the minimum expected responsibilities out of financial fiduciaries. These duties can be better explained as follows:
- Duty of care: The duty of care refers to the fiduciary's obligation to make informed decisions that work best for the client. The fiduciaries must decide what the client wants depending on their field of work and must have sound knowledge about the field before they can take any judgments for the client.
- Duty of Loyalty: This duty mandates fiduciaries to reciprocate the trust placed by their clients in them by avoiding decisions that may be selfishly motivated. The fiduciaries themselves should not hold any conflict of interest that remains undisclosed to their clients. They must also reveal any opportunities where there is a potential for them to obtain commissions.
An additional duty that fiduciaries must take care of is the duty to act in good faith. The client places his faith in the fiduciary, which must be honored back. Out of all available options, only that option should be chosen, which best fits the client’s criteria.
What is the suitability rule?
Fiduciary obligations may not be acceptable everywhere. For example, investment brokers can not fall under the category of a fiduciary. However, there is something called a suitability obligation that they must adhere to.
Suitability obligation only requires the accountable party to go after that option, which is the best fit for the client. While choosing the best option, they may not put their client’s interest above their own.
Under the suitability rule, should deliver the recommendations given after considering the client's financial outlook, future goals, purpose, and risk-taking capacity. The client must not incur additional costs, and there should not be any excessive trades on his behalf. This can lead to a situation where the professionals put their own interests above that of the client.
What happens if the responsibilities are not fulfilled?

Image source: © Mustangmarshal | Megapixl.com
Since the fiduciary is mandated by the law to follow the required duties, it becomes illegal if they are not fulfilled. Legal proceedings might take place in such a case. The court may decide to sue the fiduciary upon breach of contract.
In return, the client may receive compensation for the breach.