Definition
Related Definitions
Fast Track Designation
What is the Fast Track designation?
Fast Track designation is a process that is meant to accelerate the development and expedite the review of medicines or drugs focusing on the treatment of serious indications and capable of addressing unmet medical requirements. The purpose of this designation is to find an important new treatment for early access to the patient. The Fast Track designation addresses a comprehensive range covidof severe disease indications.
In other words, the Fast Track designation process is made to facilitate the drug development, accelerate the Food and Drug Administration (FDA) review of drugs for serious indications, and address an unmet medical need.

Establishing whether a disease is serious or not is based on assessment. In general, the judgment is based on the drug’s ability to make an impact on factors such as day-to-day functioning and survival, among others. Also, if left untreated, the condition could progress from less severe disease to a more serious one.
Some examples of serious diseases that can progress to more severe levels, if left untreated, include Alzheimer’s disease, heart failure, cancers, and AIDS. Other conditions like depression, diabetes, and epilepsy are also considered to be serious.
What is the Fast Track Program?
The Fast Track program facilitates the expedited development and review of new drugs or biological drugs that are intended to-
- Treat serious or life-threatening diseases.
- Demonstrate the potential for addressing unmet medical needs.
Sponsors or drug developers usually apply for a Fast Track designation during the investigational new drug (IND) phase of drug development.
What are the requirements to apply for Fast Track designation?
Any medicine that is being developed for treatment or prevention of an indication with no approved current treatment is directed at an unmet medical need. If there are already available treatments, a Fast Track drug must demonstrate a few benefits over the available treatment. These benefits include-
- Demonstrating superior effectiveness and impact on severe consequences or improved effect on severe outcomes.
- Preventing serious side effects or adverse effects of an already existing treatment.
- Enhancing the detection or diagnosis of a severe disease where early diagnosis results in a better outcome.
- Reducing clinically substantial toxicity or adverse drug reaction with an already available treatment that is common & triggers discontinuation of the drug.
- Capability of addressing emerging or expected public health requirements.
What is the purpose of the Fast Track designation?
Fast Track designation is an approach to make a new drug quickly available for patients suffering from serious diseases. It could be considered as an approach to avoid the progression of a serious indication to become more severe or life-threatening. There are four approaches of FDA to make new drugs available as quickly as possible, and Fast Track designation is one of these four approaches.
The remaining three are priority review, breakthrough therapy, and accelerated drug approval.
What are the incentives for a drug after it receives a Fast Track designation?
After a drug receives Fast Track designation, it is eligible for some specific incentives. These incentives help drug developer to get early approval for that particular drug. The benefits are-
- Regular meetings with the Food and Drug Administration regarding the discussion of the development plan of a drug and to make sure the collection of appropriate information required to support approval of the drug.
- The drug developer could get more frequent written communication from the FDA regarding such the design of the planned clinical trials and usage of biomarkers.
- With the Fast Track designation, the drug can get eligibility for accelerated approval & priority review if all the relevant criteria are met.
- This designation can offer rolling review authorization to the drug company. The rolling review means that a drug developer can submit completed sections of its biologics license application (BLA) or new drug application (NDA) for review by the FDA. The company does not need to wait until every section of the new drug application is completed before the full application can be reviewed.
NDA or BLA review usually does not start till the drug manufacturer has submitted the complete application to the FDA.
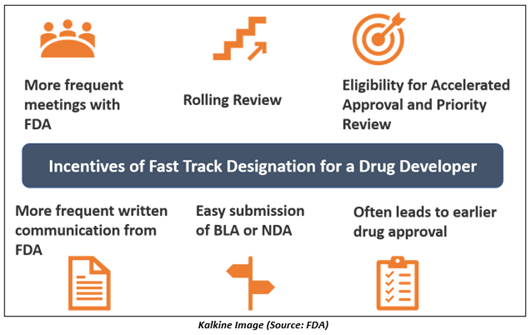
Once a drug is granted Fast Track designation, early and regular interaction between the FDA and a drug manufacturer is encouraged during the complete drug development as well as the review process. The communication frequency confirms that questions and concerns are settled immediately, often leading to earlier drug approval and access of the drug by patients.
Who can apply for Fast Track designation?
A pharmaceutical company or a sponsor that is manufacturing a drug to treat the condition with no existing therapy can request an application for Fast Track designation. The application can be started at any time throughout the process of drug development.
If the drug has significant advantages over existing therapies and the unmet medical need requirement is fulfilled, then also a drug manufacturer must apply the Fast Track designation.
After the application, the FDA will review the request and decide within two months based on whether the drug fulfils an unmet medical need in a serious indication.
Recent Examples of Drugs/Biologics receiving Fast Track designation
Fast Track designation for a vaccine against ongoing life-threatening COVID-19
Pfizer Inc (NYSE:PFE) and BioNTech SE (Nasdaq:BNTX) are developing a vaccine for the ongoing pandemic. The companies announced that two of their four investigational vaccine candidates BNT162b1 and BNT162b2, from their BNT162 mRNA-based vaccine program, received Fast Track designation from the FDA. The vaccine developers stated that this designation was granted based on the initial data from Phase 1/2 clinical trials of BNT162 as well as animal immunogenicity studies.
With this designation, the vaccine developers got the opportunity to work closely with the FDA through the clinical development of their BNT162 mRNA-based vaccine program.
Bristol Myers Squibb Granted Fast Track designation for Opdivo (nivolumab) plus Yervoy (ipilimumab) Combination
Bristol Myers Squibb had received a Fast Track designation grant from the FDA for Opdivo plus Yervoy administered concomitantly for the first-line treatment of patients having metastatic or recurrent NSCLC (non-small cell lung cancer). Additionally, the FDA has also granted priority review to the combination of Opdivo plus Yervoy.
