Definition
Related Definitions
Decision Tree
What is a Decision Tree?
A decision tree is a widely used data mining technique for classifying multiple covariates (those variables that are co-related to dependent as well as independent variables) to develop a prediction algorithm for the target variable. A decision tree helps classify the data into branch-like sections starting from the root node, internal, and leaf nodes.
Decision tree starts with a root node, and subsequently, it branches into possible outcomes. These outcomes then result in additional nodes until the correct output is achieved. The biggest advantage of using a decision tree is that it presents the necessary information to the user in the most effective manner.
A decision tree is amongst the most supervised machine learning algorithm that is used for regression analysis and problems related to the classification of variables.
Let us consider an example to understand whether an individual is fit or not fit based on food choice and lifestyle using a decision tree:
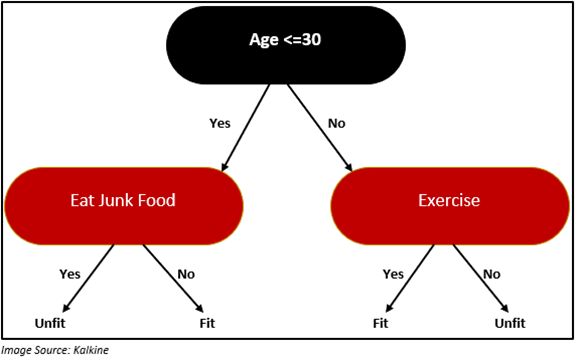
From the above decision tree, one can quickly figure out that an individual whose age is less than or equal to 30 years and does not eat junk food is healthy. On the other hand, a person over the age of 30 years and exercises regularly is fit, and if the person does not exercise, then he/she is considered unfit.
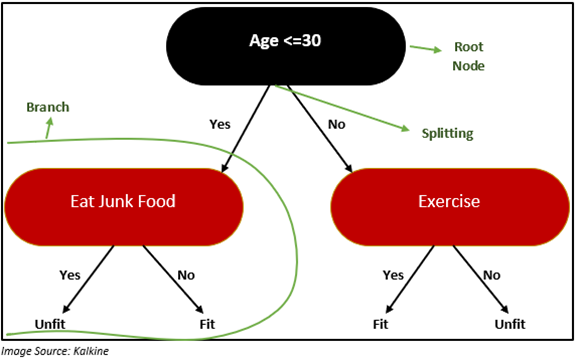
In the above example, “Age” is the root node, “Eat Junk food” and “Exercise” are the decision node. “Fit” and “Unfit” are terminal nodes.
Let us understand the key terms used in the decision tree.
- Root Node: Root node refers to the attribute from where the data is divided into two or more sets.
- Decision Node: Decision node refers to the sub-node which comes after splitting a node or a sub-node.
- Terminal Node or Leaf Node: Termina node as the name suggests is the end node of the decision tree.
- Splitting: Splitting refers to a point from where a node is divided into sub-nodes based on conditional statements like if-else.
- Branches: Branches are also known as sub-tree is a part of the entire decision tree.
- Pruning: Pruning refers to the technique where a sub-node is removed from the tree.
What is the use of decision tree?
A decision tree is generally used by businesses while making any decision. Practically, there are ‘n’ numbers of solutions possible using a decision tree, which can be adopted by companies as well as the government of any nation.
How does a decision tree work?
After understanding the decision tree, its components, and its application, one would like to know how a decision tree works.
In this section, we would look at specific steps that are followed while making a judgement using a decision tree. Let us consider an example where we have to decide whether Alan should accept a new job role or not using a decision tree. We would follow the below-mentioned steps:
- We would look at the dataset and choose one such attribute from the dataset, which even a common person can see and understand with some school level programming understandings.
- Place this attribute of the dataset as the root node.
- In the next step, we would split the training data into subsets. Training data refers to the material that enables the computer to process information.
- Subset should be split in a way that each subset has data with the same value of an attribute.
- We would continue to follow the above steps again and again till we reach a leaf node or terminal node.
Example:
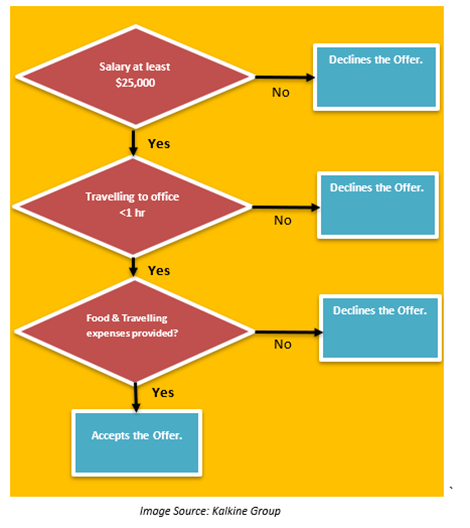
Alan has an offer of $25,000, and we have to decide if Alan should accept the offer or not. In the below diagram, whether Alan would take the new role or not would not only depend on the salary offered, but he would also look at other convenience like travel time, food and travelling expenses provided by the company or not.
Why should one use a decision tree?
Using a decision tree has several advantages. Some of them are highlighted below:
- As compared to other algorithms, decision trees require considerably less effort for preparing data in the pre-processing phase.
- In a decision tree, there is no need for data normalization.
- There is no need to size the data.
- In case any data is not available, then it would not impact the process of building a decision tree.
- A decision tree is very intuitive and easy to explain to the technical team engaged in preparing relevant coding or any program.
What are the drawbacks of using a decision tree?
- The biggest disadvantage of using a decision tree is that in the case, even if there is a small change, there could be a massive change in the structure of the decision tree causing instability.
- There might be a possibility that the calculation in case of the decision tree can be highly complex as compared to other algorithms.
- A decision tree requires more time to train the model.
- Such models are quite complicated and consume more time.
- Decision tree algorithms are not enough to apply regression analysis and predict any continuous values.