Definition
Related Definitions
Days Payable Outstanding
Days payable outstanding (DPO) is an accounting relationship showing the average number of days a company takes to pay off its' bills or invoices from trade creditors. The payables in this computation represent outstanding balances to creditors for production and office supplies or financiers. The ratio may be calculated on a quarterly, half-yearly or annual basis. It is an indicator of a company's capability to manage cash outflows.
DPO is a turnover ratio. A high resultant of this metric shows that the company is slow to pay its suppliers. It may affect its future credit capabilities, but it also means that the firm can use cash for a longer time. Extremely high DPOs may also be due to existing liquidity issues.
Summary-
- Days payable outstanding (DPO) gives the average number of days needed by a company needs to do away with its' creditor invoices and obligations.
- It is a turnover ratio and indicates the operational efficiency and cash management capabilities of a firm.
- While a high DPO ensures cash availability for operations, it also affects the credit relations with suppliers. Hence an optimum DPO as per the Industry in which the company operates must be determined.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQ)-
How is Days Payable Outstanding (DPO) computed?
The Formula for computing the ratio is as follows-

Source: Copyright © 2021 Kalkine Media
here:

Source: Copyright © 2021 Kalkine Media
For Example, suppose Company A has the following balances at first quarter end of FY19-20. Average Accounts Payable is US$500,000 & Cost of Goods Sold is US$800,000. Consider Days in the Accounting year as 360.
Then, Days Payable Outstanding for Company A using the above Formula will calculate as,
(US$500,000/ US$800,000) x (360/4) = 56.25 days, i.e. 56 days approximately.
It means Company A, on average, takes 56 days or more than one and a half months' time to dispense off its payables.
How is Days Payable Outstanding (DPO) interpreted?
Days Payable Outstanding is a critical factor of the Cash Conversion Cycle (CCC). It tells investors and analysts the number of days for which cash is locked as working capital.
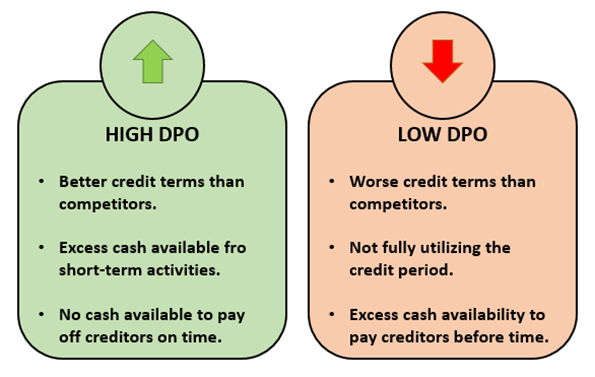
Now the DPO can either be high or low, the resulting number of days is interpreted as follows-
Source: Copyright © 2021 Kalkine Media
It is prevalent for companies to obtain raw materials and other production or office utilities on a credit basis. It is what makes up the payables balance representing a company's short or medium payment obligations in general. The DPO metric is used to measure the average time in which such obligations are nullified or settled.
A High DPO usually suggests cash availability for short-term use and increases working capital and free cash in a firm. However, this may not be optimum for a firm as it endangers the firm's relations with financiers and suppliers. Creditors may refuse to offer trade credit in the future or may become stringent with their credit policies if payment is delayed often. For a low DPO, everything is the exact reverse.
As all firms compute DPO value, a better judgement can be made by comparing it in the industry sector. It will show whether it's ok or not to have too high or too low DPO and help companies adapt to the industry practices.
What are the uses of Days Payable Outstanding (DPO)?
- It is a crucial efficiency ratio measuring average payback time to suppliers.
- It is used as an input factor to analyse the cash conversion cycle.
- The ratio is crucial for creditors to determine credit terms and restrictions if needed.
- It indicates how a company is utilising its cash position
- The ratio is an indicator of the operational efficiency of a company.
- The metric is used for industry comparison and negotiation with suppliers.
What are the Limitations of DPO?
- It doesn't reflect a clear picture of a company's bargaining power.
- Without a significant industrial comparison, its utility is restricted.
- It cannot be considered as the only reflector of the cash position of a firm.
- There is no standard value available; DPO varies significantly by Industry.
- It is easily influenced by micro & macro factors like negotiation power and industrial economics.
How can a company improve its DPO?
To improve the day's payable outstanding position, a company needs to optimise credit terms and its cash availability. The company has free up working capital and manage costs well to reduce the complexity in accounts payable dispensing.
If DPO is to be increased, the company must try to negotiate on the creditor's invoicing process, set up supplier lists and get the best possible payment terms.
To benefit and still close that gap between invoice receipt and payments company can undertake the following steps-
- Negotiate & ask for early payment discounts from Suppliers- Suppliers chosen must be from a preferred list who have a good trade relation with the company. Based on this relationship, the company must negotiate payment terms and ask for early payment discounts. This will save some amount of outflows.
- Ask for a change in payment terms- efforts must be made to make the lifecycle of a payable flexible. It can be beneficial for the debtor and creditor as payments will be made as per cash availability before the actual payment date. It will reduce the debt burden and improve cash availability with the creditor.
- Automated payment reminders- in the current era of computerised accounting software, a company can set payment reminders in the system to avoid delays. This will enable better payable management and reduce the amount of delayed and excess outstanding. There are also features available for payment receipt confirmation from the creditor's side.
- Internal & External reviews for credit control- Auditors can be appointed as a part of internal controls to keep an eye on overdue payables. This will enhance the credibility of a firm and reduce the DPO number by ensuring on-time payments. Regular reviews will keep a check on outstanding and cash.
- Improve inventory control- this is essential to reduce the need for working capital. Once there is no extra need for operational funds, the number of payable balances will go down automatically. The Japanese' just in time' inventory technique is one such method. It not only aligns inventory but, in turn, reduces outstanding payables.
