Definition
Related Definitions
Cybersecurity
What Is Cybersecurity?
It is only when they go wrong that machines remind you how powerful they are - Clive James
The content you are reading is written using a computer and shared via network servers. Almost everything we do, we depend upon today, is codified by data. As we become more and more dependent on technology, the global cyber threat is increasing and evolving continuously. Hence today, choosing cybersecurity techniques are more of a necessity than a choice.
RELATED READ: Cybersecurity and the Requirement of a Resilient Environment in Australia
Cybersecurity is a pool of technologies, processes and practices which are designed to protect networks, electronic devices, data and programs from digitally processed malicious attacks, damages or any unauthorised access. Cyberattacks are engineered to access or destroy the official/personal information, and it can be misused to extort money from the users or to interrupt normal processes.
Society is already intertwined with not only the internet but to the evolving age of automation, Big Data, and the Internet of Things (IoT). As technology has played a substantial role in bettering our lives, it also brings threats. It has become a paramount priority to protect our technology from cybercrimes, industrial espionage, and cyberattacks.
ALSO READ: Technology has changed the way we work amid the COVID-19 crisis: A look at in-demand technologies
What are the different forms of cyber threats?
There are three typical cyber threats identified:
- Cybercrime in which a person or a group targets a system to commit financial fraud or cause disruption. Phishing scams, identity theft, online harassment or cyberbullying, cyberstalking and invasion of privacy are few common cybercrimes undertaken using computers, phones and the internet.
- Cyberattacks include malicious attacks to steal data or breach a computer to launch an attack on another system.
- Cyber terrorism is undertaken to infiltrate the virtual world in order to cause panic or fear.
Why do we hear about Cybersecurity so often?
Executing effective cybersecurity measures is considered challenging nowadays as the number of devices has increased more than the number of people in the world and the cyber attackers are becoming more innovative than before.
Notably, a constructive cybersecurity initiative has multiple layers of protection spread across various aspects. Computers, networks, programs or data are protected using these measures. For instance, in an organization, not just the processes and technology but its data and the peoples' information are also protected to create an effective defense from cyberattacks. The security system integrates these across various platforms in order to function in the below domains:
RELATED READ: Knock Knock! Cybercriminal at Your Doorstep
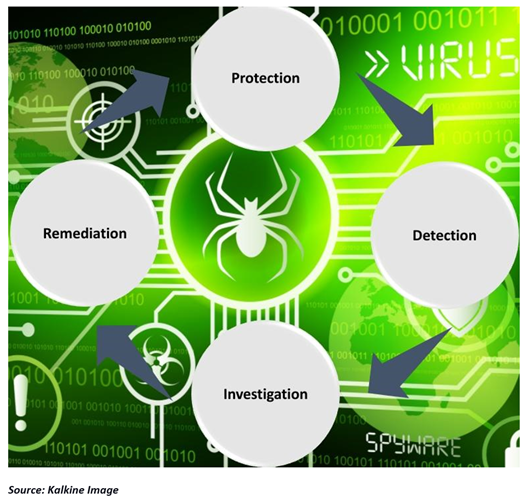
The computers and phones we use, planes we fly, schools we study, offices we work at, banks we keep our money safe, and overall the society’s functioning are all primarily dependent on technology. Hence the issue of cybersecurity stands as vital as the technology itself. If we want to protect our way of life from being hacked, manipulated, and controlled, cybersecurity is required.
With technology reaching door to door, the hacking has become more common. Any system can be breached by hacking it via one click on an unwanted email. The person clicking on it may not know what it has gotten into; the firewall and security softwares may not help you by then. Mobile call fraud is also widespread when a person may innocently end up giving its personal information which can be used to hack bank or email accounts or blackmailing.
Why is cybersecurity critical?
- Individual-level safety: In the world full of technological advances, even a single security camera installed on the corner of the road for your protection can be hacked and used for malpractices, which is why cybersecurity is essential to safeguard anything and everything in the digital world.
At an individual level, phishing can take place to extract personal information or financial statements by a fraudulent person disguised as a legitimate representative. Not just the computer system but the autonomous cars and transports system can also fall in the hands of hackers and cybercriminals to abuse. Wearables such as smartwatches which capture data related to health, location can be targeted for phishing or identity theft.
- System safety: Malware attacks on the computer system are the most common attacks in order to spread various types of malware software such as virus, trojan, spyware, ransomware, adware and botnets. The harmful software may not just damage the system and the data but also record videos and audios on your system without your knowledge.
Man-in-the-middle attacks are a kind of a communication breach where the criminal can violate the communication privacy and record calls between two individuals and use it to blackmail.
- Industry and infrastructure: One cyberattack can cripple the entire infrastructure and attack organizations, losing millions of dollars and the reputation. Ransomware and Cryptowares extort money or steal data worth billions. Identity theft is one of the frequent crimes executed to gain access to financial details and commit fraud.
- Cyberwarfare: As the world is moving towards technological advances and economic developments, physical warfare has now transitioned into Cyberwarfare which includes - cyberespionage, cyberwarfare, and cyberterrorism. Many governments have faced and are still facing an increased number of Cyberwarfare attempts. Be it an individual, or government group or any organisation, anyone can knowingly or unknowingly play a part in this virtual warfare, and it can be as damaging as the traditional physical wars.
How can we address Cybersecurity?
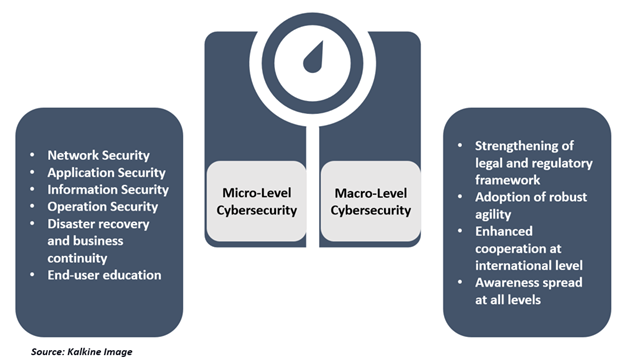
Micro Level:
- With network security, one can safeguard computers from hackers or criminals from attacking systems or stealing the data.
- Application security will keep the software and devices safe from external threats.
- Whereas with information security one can protect the integrity and privacy of the data.
- In operation security, the system is protected while handing and accessing the data.
- Disaster recovery and business continuity is a functionality pertaining to the organizations’ decisions and responses to the cyberattacks, loss of data or industrial espionage.
- End-user education addresses the essential part of this process - the people. It's necessary to provide adequate information and enable people to follow good security practices.
Macro Level:
- There is a grave need for strengthening of legal and regulatory framework and adoption of robust agility in developing or updating national cybersecurity strategies.
- Cybersecurity requires enhanced cooperation at international level.
- Awareness spread at all levels forms the crux of this initiative.
