Definition
Related Definitions
Brokerage Fee
What is a brokerage fee?
A broker charges a brokerage fee for providing specialised services and executing transactions. Brokers charge for a variety of services, including sales, acquisitions, negotiations, consultations, and delivery.
It is imposed in various businesses, including real estate, insurance, financial services, and delivery services.
Summary
- A broker charges a brokerage fee for offering specialised services and completing deals.
- The broker fee is calculated as a percentage of the total transaction amount, a flat charge, or a mixture of the two.
- Full-service, discount, and internet brokers are the three primary financial securities sector brokers that charge brokerage fees.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
What are the various types of a brokerage fee?
A broker fee, also called a brokerage fee, is calculated as a percentage of the total transaction amount, a flat fee, or a combination of the two. Brokerage costs vary depending on the type of broker and sector.

Source: © Theaphotography | Megapixl.com
A brokerage fee is often a flat fee in the real estate market, or a specified percentage charged to both the buyer and the seller. Mortgage brokers assist potential borrowers in finding and obtaining mortgage loans, and their fees range from 1% to 2% of the loan amount.
In the insurance market, unlike an agent, a broker represents the customer's interests rather than the insurers. Customers' demands are met by brokers, who charge a fee for their services in obtaining the most satisfactory insurance coverage. Brokers may occasionally receive commissions from both the individual and the insurer purchasing the insurance policy. In the insurance industry, a brokerage fee is levied to oversee investments or enable trade.
Source: © Strels | Megapixl.com
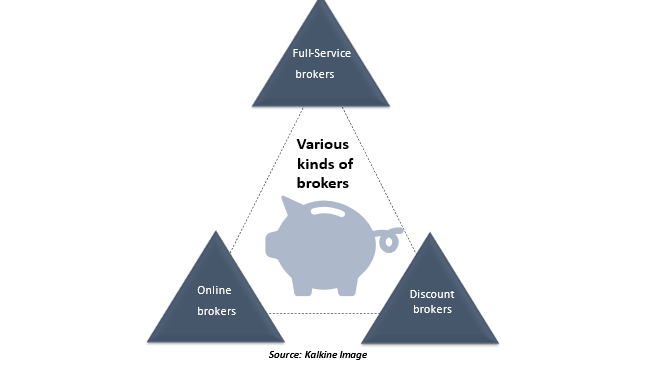
What are the different kinds of brokers who charge brokerage fees?
Full-Service brokers
They earn the highest brokerage fee by providing a wide range of products and services in-person or over the phone, such as preparation, tax counselling, estate planning and other financial services.
Discount brokers
They do not provide investment advice and have a smaller product selection than full-service brokers. Hence their costs are lower. Discount brokers charge each trade transaction a flat fee. The flat fee per trade ranges from $5 to $30, and account maintenance costs are typically around 0.5%.
Internet brokers
Because their primary job is to allow investors to do online trading with limited customer assistance, online brokers have the lowest brokerage costs. Although many online brokers have eliminated a specific commission cost for stock trading, commission costs for options and futures trading remain. Fee varies and may be calculated on a per-share or per-contract basis. Account maintenance costs range from zero to 50 dollars per account.
How do you calculate the brokerage fee?
To facilitate trading, brokers receive a brokerage fee from traders and investors while buying and selling securities.
However, most brokers charge a portion of the trading value as a brokerage fee, with the percentages varying depending on the scope of the deal value. The following is the formula for calculating brokerage fees in the stock market:
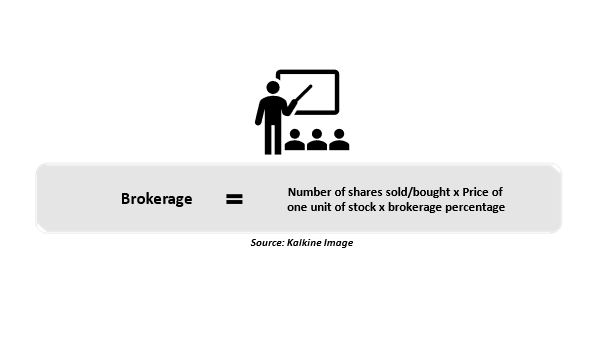
For example, Alexandra decides to buy 40 shares of Commonwealth Bank of Australia at AU$ 4,000 apiece and sells them for AU$ 4,200 within 20 days. She does that through Broker A, who charges a brokerage fee of 0.8%.
Alexandra’s overall trade value, in this case, is:
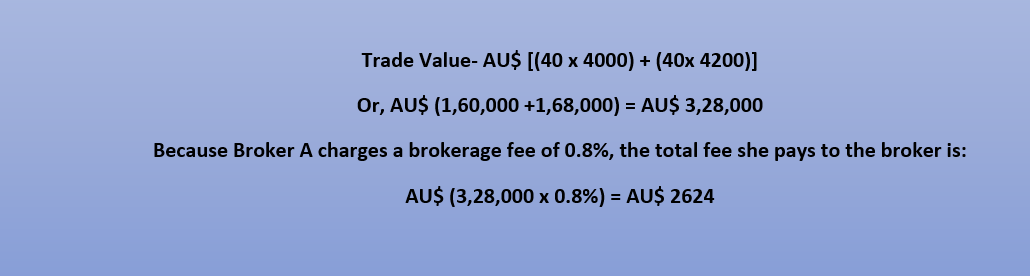
As a result, Alexzandra would pay AU$ 2624 as a brokerage fee for transactions totalling AU$ 3,28,000.
What are the variables on which the brokerage calculation is based?
The following are the factors that influence brokerage calculations:
Price of sale and purchase
The sale or buy price of a single security unit determines the brokerage commission, which is directly proportionate to the brokerage.
The number of transactions
The transaction volume significantly impacts brokerage calculations, whether they're done manually or with a brokerage calculator. This is because the brokerage amount rises in proportion to the volume. When investors trade in substantial amounts, however, specialised brokers will lower the percentage commission.
What are the advantages and drawbacks of the brokerage fee structure?
While investors should generally seek lower cost investing options, the fact that a broker's fees are higher than those of its competitors should not disqualify it. While the fee may irritate some investors, active day traders may be ready to pay more for trading tools and access to more investments. In addition, long-term investors may be willing to pay a premium for more in-depth advice.
Fee and additional expenses may eat into an investor's capital, but they're paying for products that help them make better investment decisions. An active investor may require fundamental and technical analysis, including earnings estimates, historical financial performance, industry dynamics, and competitor research.
