Definition
Related Definitions
Anti Money Laundering (AML)
What is Anti-Money Laundering (AML)?
Anti-money laundering (AML) encompasses laws, regulations, procedures, and policies meant to discourage violators from indulging in financial crimes and money laundering activities. AML is incorporated within the system of national and local government with an aim to monitor a potential violator or fraudulent activities.
Countries have different AML policies which have to be followed by the companies. To ensure compliance with AML regulations, organisations have created AML department to address non-compliance. Non-compliance often leads to government scrutiny.
What is the objective of Anti-Money Laundering?
Criminals attempt to introduce illicit money into the financial system and hide the sources of illicit funds. Anti-money laundering aims to deter such criminal activities and detects the true source of the funds.
AML is generally employed by the compliance, legal, and financial sectors to introduce or develop control systems that an organisation should implement with an aim to identify and then stop the activities which can result in money laundering.
The need for AML policies and procedures leveraged as customers have moved to online products and services. Since the products and services are exchanged through online platforms, it has become easy for the violators to introduce illegitimate money into the system. If an organisation complies with the stated AML guidelines, the chances of money laundering can be reduced significantly.
AML regulatory benefits are not only limited to money laundering minimisation but also help the organisation to undertake its operations in an effective and efficient manner. It has become a minimum requirement to follow the AML practices to commence business activities at the global level. Compliance with AML regulations is mandatory for all organisations. The banking and FinTech sectors have to strictly follow the same, otherwise, hefty penalties are lived on them by regulatory bodies. RegTech (Regulatory Technology) and compliance officers are deployed to ensure that institutions meet the regulatory requirements and create a positive image in the open market.
How is Money laundering done?
Money laundering stands for the methods which are used to legalise the funds which have been obtained from illegal activities. By money laundering, violators aims at hiding the crime and source of funds.
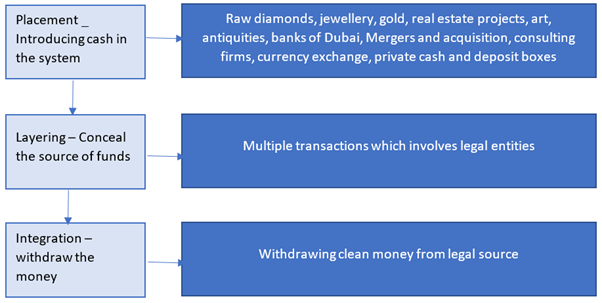
A study by Teichmann (2017) indicated that raw diamonds, jewelery, gold, real estate projects, art, antiquities, banks of Dubai, Mergers and acquisition, consulting firms, currency exchange, private cash, and deposit boxes are the major methods employed for money laundering.
To identify the money laundering sources and minimise its negative impact, AML regulations are introduced for global, national, and local regulators. These regulations keep on evolving as per the changing trend of fraudulent activities. To illustrate: AML regulations were changed in 2020 because the cases of fraudulent activities increased significantly after the COVID-19 pandemic.
What is the process of Money Laundering?
Money laundering is undertaken to convert a large amount of illegal funds into clean money. Significant amount of risk is involved in the process as banks have to report to regulators when a large transaction takes place or other suspicious activity is observed. Therefore, a procedure is adopted by criminals to enter the illegal cash into the banking system. Chiefly, three steps are adopted, that is, Placement, layering, and integration.
- Placement: The cash is introduced into the financial system through different methods.
- Layering: The source of cash is concealed by conducting numerous transactions and each layer has a legal participation.
- Integration: It is the final stage in which the criminal withdraws the clean money and utilises the same for different purposes.
Copyright © 2021 Kalkine Media Pty Ltd
There are various techniques to launder money. For example, an organisation manipulates (inflate) its financial records and the balance is used for introducing funds in the system.
What are the techniques of Anti-Money Laundering?
Numerous procedures are introduced by regulators to achieve AML goals and they have to follow the stated procedures.
The United Nation Office on Drug and Crime (UNODC) specifies the techniques and procedures to be adopted by the organisations to spot and prevent transactional crime like money laundering. Furthermore, commitment to UNODC includes the adoption of frameworks for law cooperation, and legal assistance. It also focuses on the technical assistance and training for upgrading the capacity of regulators.
- Know-your-customer is incorporated by the organisations to prevent money laundering. It involves learning about the customers and continuously monitoring their financial activities. On the basis of the evaluation of financial behaviour, red flags are raised when a deviation is observed in the behaviour of the customer. Non-compliance with the KYC norms results in financial terrorism and hefty penalties by the regulators.
- Financial institutions keep records of all the transactions and combined them with the potential of artificial intelligence (AI) to identify suspicious activity. Softwares have the potential to categorise the customers on the basis of suspicious activities and the actions are taken accordingly. Furthermore, technological development, like integration of big data, AI, or integration of AI, and Blockchain technology, helps in identifying suspicious activities at the integration stage.
- Many banks have the policy of holding period, that is, banks hold the money for a specified time (usually 5 days). The holding period allows banking institutions to tackle the risk of money laundering.
How to design a corporate AML Compliance Program?
An organisation can create a compliance program, which will help to identify and evaluate impending risks and legal obligations a company is exposed to. A compliance program should be designed on the basis of following 4 foundation blocks.
- Designated Compliance executive: An experienced compliance officer should be appointed, who will have the authority to supervise effectively the execution of AML policies in a company. The Officer should have the capability to effectively communicate with management and auditors. The AML policy recommendations required to make the process more effectively and de-risk the company.
- Regular review of AML processes: The Anti-Money Laundering program should regularly evaluate the company’s policies and procedures to ensure AML program is effective. The company should make its employees aware of their roles and responsibilities for them to adhere to compliance and follow proper business due diligence process.
- Awareness of AML procedures to Employees: Organisations should provide tailored training to employees whose work requires heavy compliance adherence. Working knowledge of AML processes by employees is a necessity for the compliance program to run effectively. Every amendment should be duly communicated to employees. Maintaining a log of training provided also helps in creating a sound AML compliance program.
- Third-party Audits: An organisation should engage a qualified and experienced third-party company to evaluate the AML compliance program yearly. However, companies operating in high-risk areas should evaluate their AML compliance program more frequently.
